How Autoimmune Gum Problems Affect Oral Hygiene in 2025
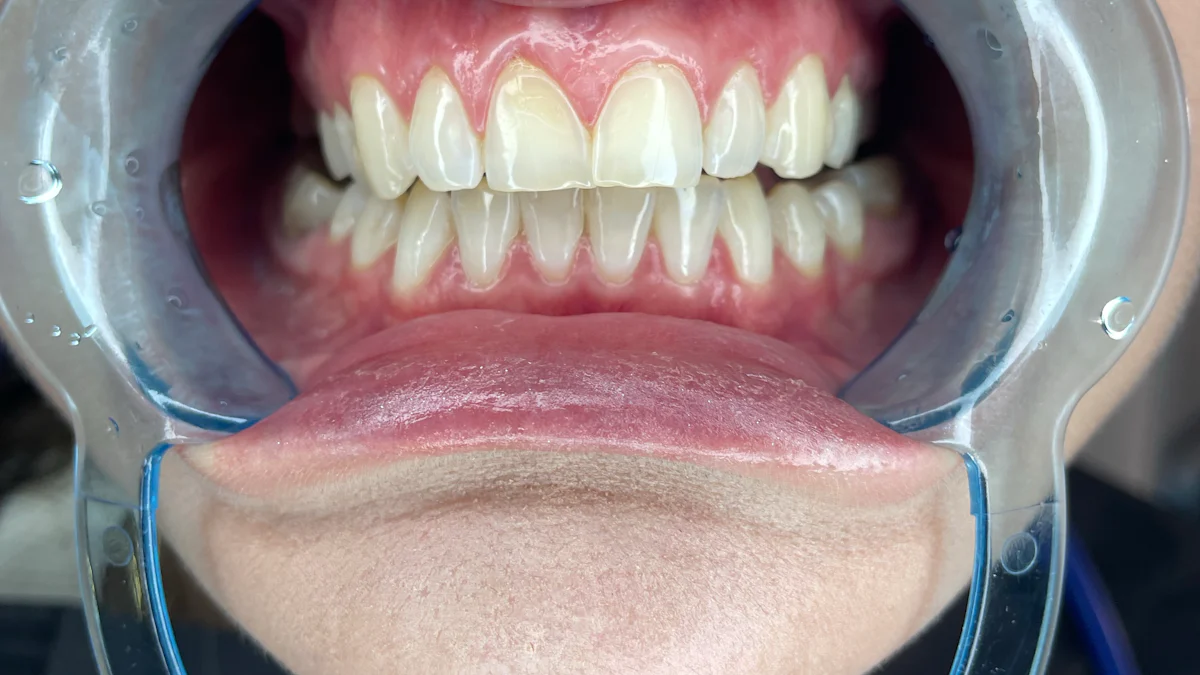
Autoimmune gum problems can have a significant impact on your oral health. These issues often lead to inflammation, bleeding, and dry mouth, all of which heighten the risk of infections. For instance, Sjögren’s syndrome decreases saliva production, resulting in a dry environment that fosters cavities and harmful plaque buildup. Autoimmune diseases such as lupus or Crohn’s disease may also cause mouth ulcers, damage to gum tissue, and even hidden oral complications due to reduced pain sensitivity. Without proper management, autoimmune gum problems can weaken your gums and teeth, making daily dental care more difficult. Recognizing how autoimmune responses contribute to gum problems is essential for maintaining your oral health.
Autoimmune Diseases and Their Impact on Oral Health
Autoimmune diseases can significantly affect your oral health. These conditions occur when your immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissues in your body, including those in your mouth. This can lead to a range of oral health issues, from gum inflammation to severe tissue damage. Understanding how autoimmune diseases impact your gums and teeth is crucial for managing these challenges effectively.
What Are Autoimmune Diseases
Autoimmune diseases are conditions where your immune system, which normally protects you from harmful invaders like bacteria and viruses, begins attacking your own tissues. This immune response can target various parts of your body, including your gums, salivary glands, and oral tissues. Some of the most common autoimmune diseases that affect oral health include:
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE): Causes oral discoid lesions and gingivitis.
Sjögren Syndrome: Reduces saliva production, leading to dry mouth (xerostomia).
Pemphigus: Characterized by painful blisters in the mouth.
Behcet Disease: Triggers painful mouth sores resembling canker sores.
Crohn's Disease: Results in painful lesions in the mouth.
Oral Lichen Planus: Appears as lacy white patches and painful sores.
These conditions can make your gums more susceptible to infections and other complications. For example, Sjögren’s syndrome often leads to dry mouth, which increases the risk of cavities and gum disease. Pemphigus and Behcet disease can cause painful sores, making it difficult to maintain proper oral hygiene.
How Autoimmune Diseases Affect the Immune System
Autoimmune diseases disrupt your immune system’s ability to protect your gums and oral tissues. Instead of defending against harmful bacteria, your immune system may attack the tissues in your mouth, leading to inflammation and damage. This can result in conditions like gingivitis, gum disease, and even tooth loss.
Several autoimmune diseases, including lupus, Crohn’s disease, and scleroderma, are closely linked to gum inflammation. This inflammation weakens the gums, making them tender and prone to bleeding. Treatments for autoimmune diseases, such as immunosuppressive medications, can further compromise your immune system. This makes it harder for your body to fight infections, leaving your gums vulnerable to harmful bacteria.
The Link Between Autoimmune Diseases and Gum Health
The connection between autoimmune diseases and gum health is supported by scientific research. For instance, Sjögren’s syndrome often leads to severe dry mouth, which creates an environment where harmful bacteria can thrive. Rheumatoid arthritis, another autoimmune condition, can cause inflammation in the jaw, affecting your ability to chew and maintain oral hygiene.
A study conducted by Felipe Andrade, M.D., Ph.D., at Johns Hopkins University revealed that chronic gum infections might trigger the inflammatory autoimmune response seen in rheumatoid arthritis. The study identified a process called hypercitrullination, which occurs in both periodontal disease and rheumatoid arthritis, as a shared factor. This suggests that gum disease may not only result from autoimmune conditions but could also contribute to their development.
Additionally, research shows that individuals with higher levels of plaque are more likely to develop autoimmune diseases over time. While the exact cause-and-effect relationship remains unclear, this correlation highlights the importance of maintaining good oral hygiene to reduce the risk of autoimmune-related gum problems.
Common Autoimmune Gum Problems
Autoimmune gum problems can manifest in various ways, often leading to discomfort and challenges in maintaining oral health. These issues arise when your immune system mistakenly attacks the tissues in your gums, causing inflammation, sensitivity, and even tissue damage. Understanding these common problems can help you recognize symptoms early and take steps to protect your oral health.
Gum Inflammation and Swelling
Gum inflammation is one of the most noticeable signs of autoimmune gum problems. When your immune system targets the tissues in your gums, it triggers an inflammatory response. This can cause your gums to become red, swollen, and tender to the touch. Conditions like lupus and oral lichen planus often lead to this type of inflammation.
Swollen gums can make it difficult for you to eat or brush your teeth comfortably. The inflammation also creates an environment where harmful bacteria thrive, increasing your risk of gum disease. If left untreated, chronic gum inflammation can progress to more severe conditions, such as periodontitis, which may result in tooth loss.
Bleeding Gums and Sensitivity
Bleeding gums are another common symptom of autoimmune diseases that affect oral health. You might notice bleeding when brushing or flossing your teeth. This occurs because autoimmune conditions weaken the gum tissues, making them more prone to damage.
Sensitivity often accompanies bleeding gums. You may feel discomfort when consuming hot, cold, or spicy foods. Autoimmune diseases like Sjögren’s syndrome and rheumatoid arthritis can exacerbate these symptoms by reducing saliva production, which normally helps protect your gums and teeth. Without adequate saliva, your gums become more susceptible to irritation and infection.
Gum Recession and Tissue Damage
Autoimmune diseases can also lead to gum recession, where the gum tissue pulls away from your teeth. This exposes the roots of your teeth, making them more vulnerable to decay and sensitivity. Gum recession often occurs in conditions like scleroderma and pemphigus vulgaris, where the immune system attacks the connective tissues in your mouth.
Tissue damage caused by autoimmune responses can result in permanent changes to your gums. Over time, this damage may lead to tooth loss or the need for advanced dental treatments. Recognizing the early signs of gum recession, such as longer-looking teeth or increased sensitivity, is crucial for preventing further complications.
Dry Mouth and Its Effects on Oral Health
Dry mouth, also known as xerostomia, is a common issue for individuals with autoimmune diseases. It occurs when your salivary glands fail to produce enough saliva, leaving your mouth feeling parched. This condition often stems from disorders like Sjögren’s syndrome, where the immune system attacks the salivary glands. Medications used to manage autoimmune diseases can also reduce saliva production, worsening the problem.
Saliva plays a crucial role in maintaining oral health. It washes away food particles, neutralizes acids, and helps prevent harmful bacteria from thriving. Without sufficient saliva, your mouth becomes a breeding ground for plaque and bacteria. This increases your risk of gum disease, cavities, and other dental problems. For example, Sjögren’s syndrome often leads to severe dry mouth, making it harder to flush away debris and protect your teeth.
You may notice several symptoms if you experience dry mouth. These include a persistent dry or sticky feeling, difficulty swallowing, and a burning sensation in your mouth. Your gums might feel tender or swollen, and you could develop sores or ulcers. Over time, the lack of saliva can lead to tooth decay and gum inflammation, further complicating your oral hygiene routine.
The effects of dry mouth extend beyond discomfort. When saliva flow decreases, food particles and plaque stick to your teeth more easily. This creates an acidic environment that erodes enamel and promotes tooth decay. Additionally, dry mouth can exacerbate gum inflammation, making your gums more susceptible to infections. If left untreated, these issues can progress to advanced gum disease, such as periodontitis, which may result in tooth loss.
Managing dry mouth is essential for protecting your oral health. You can stay hydrated by drinking water throughout the day and using sugar-free chewing gum to stimulate saliva production. Dental products designed for dry mouth, such as specialized mouthwashes or toothpaste, can also help. Regular dental checkups are vital for monitoring your gum health and addressing any complications early. If you suspect an underlying autoimmune condition, consult a specialist to explore treatment options.
By addressing dry mouth proactively, you can reduce its impact on your gums and teeth. Understanding how this condition affects your oral health empowers you to take steps toward better management and prevention.
Recognizing Symptoms of Autoimmune Gum Problems
Autoimmune gum problems often develop gradually, making it essential to recognize the symptoms early. Identifying these signs can help you take timely action to protect your oral health and prevent complications. Below are the key symptoms to watch for and when to seek professional help.
Early Signs of Gum Issues
The early symptoms of autoimmune gum problems may seem mild but should not be ignored. You might notice redness or slight swelling in your gums, which could indicate inflammation. Bleeding during brushing or flossing is another common early sign. This bleeding occurs because autoimmune diseases weaken the gum tissues, making them more prone to damage.
Dry mouth is another early indicator. If your mouth feels persistently dry, it could be due to reduced saliva production caused by conditions like Sjögren’s syndrome. This dryness increases the risk of bacterial growth, leading to gum inflammation and tooth decay. You may also experience mild discomfort or sensitivity when eating or drinking.
Pay attention to any changes in the appearance of your gums. For example, gums that look shiny or overly red could signal an underlying issue. Early detection of these symptoms can help you manage the condition before it progresses.
Chronic Symptoms to Monitor
Chronic symptoms of autoimmune gum problems often involve more severe and persistent issues. Gum recession is a significant concern. When your gums pull away from your teeth, it exposes the roots, making them vulnerable to decay and sensitivity. This condition is common in autoimmune diseases like scleroderma and pemphigus vulgaris.
You might also notice recurring sores or ulcers in your mouth. These can be painful and make it difficult to eat or speak. Conditions like oral lichen planus and Behcet disease often cause such symptoms. Chronic inflammation can lead to swollen, tender gums that bleed easily. Over time, this inflammation may progress to periodontal disease, increasing the risk of tooth loss.
Another chronic symptom to monitor is persistent bad breath. This could result from bacterial buildup due to dry mouth or gum disease. If you experience these symptoms regularly, it’s crucial to address them promptly to prevent further damage.
When to Consult a Dentist or Specialist
Knowing when to seek professional help is vital for managing autoimmune gum problems. If you notice persistent symptoms like bleeding gums, gum recession, or chronic dry mouth, consult a dentist. These signs could indicate an underlying autoimmune condition that requires specialized care.
You should also see a specialist if you experience severe pain, difficulty chewing, or recurring ulcers. A dentist can perform a thorough examination and may refer you to a rheumatologist or immunologist for further evaluation. Sharing your medical history, including any diagnosed autoimmune diseases, helps your dentist tailor a treatment plan to your needs.
Regular dental checkups are essential for monitoring your gum health. During these visits, your dentist can identify early signs of gum disease and recommend preventive measures. If you suspect an autoimmune disease is affecting your oral health, don’t delay seeking professional advice. Early intervention can significantly improve your quality of life.
Managing Oral Health with Autoimmune Diseases
Managing oral health with autoimmune diseases requires a proactive approach. Autoimmune conditions can make your gums more sensitive and prone to damage, but adopting the right strategies can help you maintain healthy gums and teeth. From daily hygiene practices to professional care, every step plays a vital role in protecting your oral health.
Daily Oral Hygiene Practices
Brushing and Flossing for Sensitive Gums
Sensitive gums need extra care to prevent irritation and damage. Use a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste to gently clean your teeth. Brush at least twice daily, focusing on removing plaque without harming your gums. Flossing is equally important. It removes food particles and bacteria from between your teeth, reducing the risk of gum disease. Be gentle to avoid injuring delicate gum tissue. Staying hydrated also helps combat dry mouth, a common issue in autoimmune diseases. Drinking water throughout the day stimulates saliva production, which protects your gums and teeth.
Selecting Suitable Oral Care Products
Choosing the right oral care products is essential for managing autoimmune-related gum problems. Unsuitable products can worsen inflammation or increase discomfort. Look for toothpaste and mouthwash designed for sensitive gums. Avoid products with harsh chemicals or alcohol, as they can irritate your gums and dry out your mouth. Dental products formulated for dry mouth, such as moisturizing gels or sprays, can provide relief and improve your oral hygiene routine.
Dietary Adjustments for Better Gum Health
Anti-Inflammatory Foods to Include
Your diet plays a significant role in reducing gum inflammation and supporting oral health. Include anti-inflammatory foods like leafy greens, fatty fish, and berries in your meals. These foods are rich in antioxidants and omega-3 fatty acids, which help reduce inflammation and promote gum healing. Nutritional counseling can also guide you in making dietary choices that support your immune system and improve gum health.
Foods to Avoid for Gum Health
Certain foods can aggravate gum problems and should be avoided. Sugary snacks and drinks feed harmful bacteria in your mouth, increasing the risk of cavities and gum disease. Acidic foods, such as citrus fruits and soda, can erode enamel and irritate sensitive gums. Processed foods high in salt or preservatives may also contribute to inflammation. Limiting these foods can help protect your gums and teeth.
Professional Dental Care
Importance of Regular Checkups
Regular dental checkups are crucial for managing autoimmune gum problems. Dentists can detect early signs of gum disease and provide timely intervention. Professional cleanings remove plaque and tartar that daily brushing might miss, reducing the risk of gum inflammation. Personalized care plans address the unique challenges posed by autoimmune conditions, ensuring your oral health remains a priority.
Communicating Autoimmune Conditions to Your Dentist
Sharing your medical history with your dentist is essential. Inform them about your autoimmune condition and any medications you take. This helps your dentist tailor treatments to your needs and avoid potential complications. For example, if you experience dry mouth due to Sjögren’s syndrome, your dentist can recommend specific products or treatments to alleviate symptoms. Open communication ensures you receive the best possible care for your gums and teeth.
Advancements in Autoimmune Gum Problem Management in 2025
In 2025, advancements in technology and medicine have revolutionized how autoimmune gum problems are managed. These innovations offer hope for better treatment outcomes and improved oral hygiene for individuals with autoimmune diseases.
Innovative Treatments for Gum Health
Biologic Therapies for Inflammation
Biologic therapies have transformed how inflammation in autoimmune gum conditions is treated. These therapies target specific immune responses, reducing inflammation without suppressing the entire immune system. For example, precise laboratory testing identifies oral triggers of disease, allowing for tailored treatments. Minimally invasive options, such as ozone therapy, reduce both oral and systemic inflammation. Nutritional counseling also supports your immune system, promoting overall health.
Regenerative Medicine for Gum Repair
Regenerative medicine offers groundbreaking solutions for repairing damaged gum tissue. Techniques like platelet-rich plasma therapy use your blood cells to accelerate healing and restore gum health. Stem cell treatments promote tissue regeneration, helping to reverse gum recession and repair damage caused by autoimmune diseases. Guided tissue regeneration and 3D-printed scaffolds provide frameworks for new gum tissue to grow, offering long-term solutions for severe gum damage.
Treatment Type | Description |
|---|---|
Nanotechnology-based treatments | Target bacteria at the microscopic level. |
Gene therapy | Addresses genetic factors contributing to gum disease. |
Photodynamic therapy | Uses light-activated compounds to kill harmful bacteria. |
Probiotics | Tailored for oral health to maintain a balanced microbiome. |
Platelet-rich plasma therapy | Harnesses the patient’s blood cells to speed healing and restore damaged gum tissue. |
Laser therapy | Offers a precise way to treat gum disease with less pain and faster healing times. |
Guided tissue regeneration | Uses special membranes and growth factors to encourage new gum growth. |
3D-printed scaffolds | Provides a framework for new tissue to develop. |
Emerging Oral Hygiene Technologies
AI-Driven Oral Care Tools
Artificial intelligence (AI) has enhanced diagnostic accuracy for autoimmune-related oral conditions. AI tools detect low-grade chronic inflammation that may worsen systemic conditions. These technologies analyze radiographs to identify subtle abnormalities that human practitioners might miss. By integrating AI into dentistry, you can benefit from early detection of oral health issues, reducing the risk of complications linked to autoimmune diseases.
Personalized Dental Products for Autoimmune Patients
Personalized dental products cater to the unique needs of individuals with autoimmune diseases. These products include biocompatible materials and techniques that minimize immune system triggers. Tailored dental care plans address challenges like dry mouth and gum sensitivity. Regular check-ups with knowledgeable dentists ensure early detection of oral health problems, helping you maintain optimal gum health.
Holistic Approaches to Oral Health
Holistic approaches focus on improving your overall well-being while addressing oral health. Drinking plenty of water promotes saliva production, which protects your gums and teeth. Chewing sugar-free gum stimulates natural saliva flow, reducing the effects of dry mouth. Lubricating gels and sprays can replace saliva, offering relief from dryness. An anti-inflammatory diet, rich in whole grains, leafy greens, and healthy fats, supports your immune system and reduces gum inflammation.
Tip: Gentle brushing techniques and soft-bristled toothbrushes can prevent irritation in sensitive gums. Staying hydrated and using saliva substitutes can further alleviate discomfort caused by dry mouth.
By combining innovative treatments, advanced technologies, and holistic care, managing oral health with autoimmune diseases becomes more effective. These advancements empower you to take control of your gum health and improve your quality of life.
Long-Term Strategies for Maintaining Oral Health
Long-term strategies play a vital role in preserving your oral health, especially when managing autoimmune diseases. By building consistent habits, monitoring your gum health, and staying informed about new treatments, you can effectively reduce the risks associated with gum disease and other oral complications.
Building a Consistent Oral Care Routine
Creating a reliable oral care routine is essential for managing oral health challenges caused by autoimmune diseases. Consistency helps protect your gums from inflammation and reduces the risk of gum disease. You can follow these steps to build a routine tailored to your needs:
Brush your teeth twice daily using a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste. This minimizes irritation and protects sensitive gums.
Floss gently every day to remove food particles and bacteria from between your teeth.
Stay hydrated throughout the day to combat dry mouth and promote saliva production.
Use specialized dental products, such as moisturizing gels or alcohol-free mouthwash, to address dry mouth symptoms.
Communicate regularly with your dentist and healthcare providers to manage medication side effects that may impact your oral health.
Personalized care is key. For example, if you experience gum inflammation due to an autoimmune disease, your dentist may recommend specific products or techniques to alleviate discomfort. By following these practices, you can maintain healthy gums and teeth despite the challenges posed by autoimmune conditions.
Monitoring Gum Health Over Time
Regularly monitoring your gum health allows you to detect potential issues early and take action before they worsen. Autoimmune diseases can cause gradual changes in your gums, so staying vigilant is crucial. Several tools and methods can help you track your gum health effectively:
Method/Tool | Description |
|---|---|
Biocompatibility Testing | Ensures dental materials are safe for autoimmune patients. |
Laser Treatments | Minimally invasive therapies for treating gum diseases. |
Nutritional Counseling | Supports immune system health, which can impact gum health. |
Ozone Therapy | Integrative therapy that may help in reducing inflammation and supporting gum health. |
Specialized Dental Care | Focused on the unique needs of autoimmune patients, including the removal of harmful materials. |
These tools not only help you monitor your gum health but also provide targeted solutions for managing symptoms. For instance, ozone therapy can reduce inflammation, while nutritional counseling supports your immune system. Regular dental checkups further ensure that any changes in your gum health are addressed promptly.
Staying Updated on Research and Treatments
Advancements in dental care and autoimmune disease management continue to emerge, offering new hope for patients. Staying informed about these developments can help you make better decisions about your oral health. Recent research highlights several effective treatments for autoimmune gum problems:
Evidence Type | Findings |
|---|---|
Non-surgical periodontal treatment (NSPT) | Reduces disease activity scores in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and psoriasis (PSO). |
Inflammatory markers | Moderate evidence of decreased CRP and ESR levels post-NSPT in RA and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). |
Quality of life | Inconsistent evidence showing no effect on QoL measures for RA and PSO. |
Clinical guidelines | Limited guidelines available, with one focusing on Sjögren’s syndrome and others addressing RA, lupus, and scleroderma. |
By staying updated, you can discuss these options with your dentist and explore treatments that align with your needs. For example, non-surgical periodontal treatments have shown promise in reducing inflammation linked to autoimmune diseases. Regularly reviewing new studies and clinical guidelines ensures you remain proactive in managing your oral health.
Tip: Subscribe to reputable dental health journals or follow updates from organizations like the American Dental Association to stay informed about the latest research and treatments.
By adopting these long-term strategies, you can effectively manage your oral health and reduce the impact of autoimmune diseases on your gums and teeth. Consistency, vigilance, and knowledge are your best tools for maintaining a healthy smile.
Autoimmune diseases present unique challenges to your gum health and oral hygiene. These conditions often lead to issues like dry mouth, gum disease, and inflammation, which increase the risk of cavities and infections. Proactive care plays a crucial role in mitigating these effects. Regular dental visits, diligent oral hygiene, and a diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods help protect your gums and teeth.
Advancements in 2025 offer new hope for managing autoimmune gum problems. Innovations like biologic therapies, regenerative medicine, and AI-driven tools empower you to take control of your oral health. Personalized treatment plans tailored to your needs ensure effective management of symptoms. By recognizing early signs and adopting these strategies, you can maintain a healthy smile despite the challenges posed by autoimmune conditions.
Note: Every individual's experience with autoimmune diseases is unique. Collaborating with healthcare providers to create a personalized care plan is essential for long-term success.
FAQ
What is the connection between autoimmune diseases and gum health?
Autoimmune diseases cause your immune system to attack healthy gum tissues, leading to inflammation, swelling, and damage. Conditions like lupus, Sjögren’s syndrome, and rheumatoid arthritis increase the risk of gum disease, dry mouth, and infections, making oral hygiene more challenging.
Can autoimmune diseases cause gum recession?
Yes, autoimmune diseases like scleroderma and pemphigus vulgaris can lead to gum recession. The immune system attacks connective tissues, causing gums to pull away from teeth. This exposes tooth roots, increasing sensitivity and the risk of decay.
How does dry mouth affect oral health in autoimmune patients?
Dry mouth, or xerostomia, reduces saliva production, which is common in conditions like Sjögren’s syndrome. Saliva protects teeth by washing away bacteria. Without it, harmful bacteria thrive, increasing the risk of cavities, gum disease, and bad breath.
Are there specific dental products for autoimmune-related gum issues?
Yes, products like fluoride toothpaste, alcohol-free mouthwash, and moisturizing gels help manage symptoms. Specialized products for dry mouth and sensitive gums reduce irritation and improve oral hygiene for autoimmune patients.
How can diet improve gum health for autoimmune patients?
Eating anti-inflammatory foods like leafy greens, berries, and fatty fish reduces gum inflammation. Avoid sugary and acidic foods, as they worsen gum problems. A balanced diet supports your immune system and promotes healthier gums.
Should I inform my dentist about my autoimmune condition?
Absolutely. Sharing your autoimmune diagnosis helps your dentist tailor treatments to your needs. They can recommend suitable products, monitor gum health closely, and address complications like dry mouth or gum inflammation effectively.
Can gum disease worsen autoimmune conditions?
Yes, gum disease can trigger systemic inflammation, potentially worsening autoimmune conditions like rheumatoid arthritis or lupus. Maintaining good oral hygiene reduces this risk and supports overall health.
What are the early signs of autoimmune gum problems?
Early signs include red, swollen gums, bleeding during brushing, dry mouth, and mild sensitivity. Recognizing these symptoms early helps you take action to prevent severe gum disease or tissue damage.
Tip: Regular dental checkups and proactive care are crucial for managing autoimmune gum problems effectively.
See Also
Exploring The Deadly Risks Of Gum Disease In 2025
A 2025 Handbook On Homeopathic Treatments For Gum Disease
The Impact Of Stress On Gum Disease And Oral Health
Natural Versus Conventional Treatments For Gum Disease In 2025
