Can Gum Disease Kill You Understanding the Risks in 2025
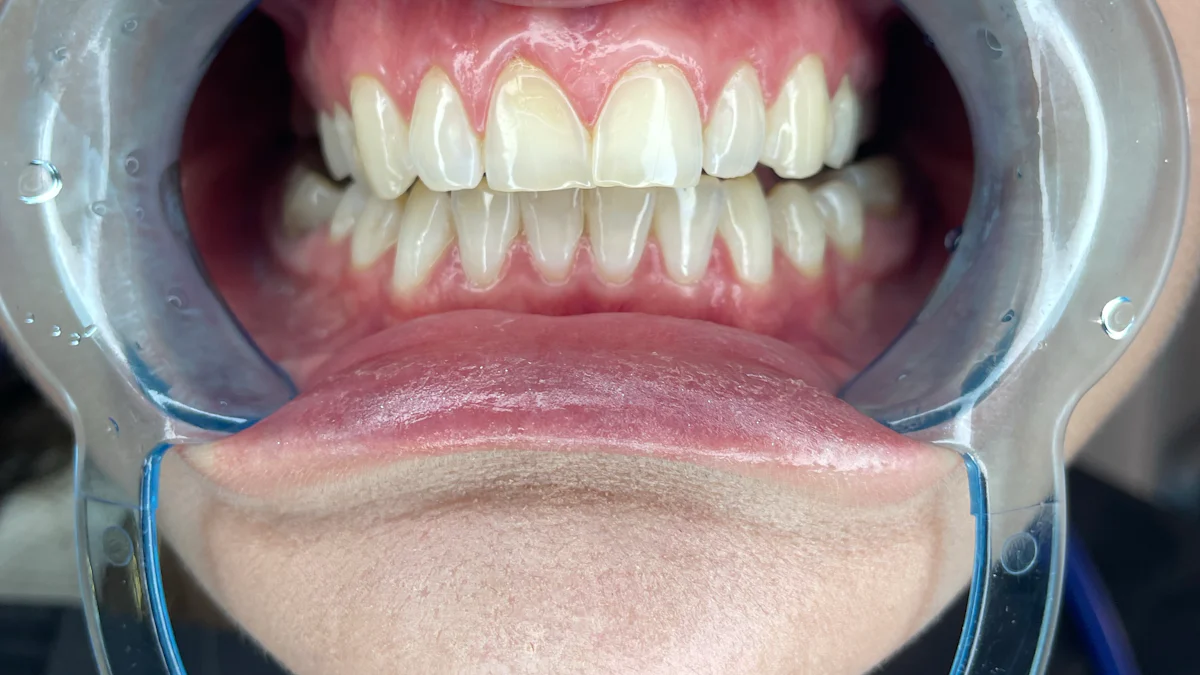
Gum disease may seem like a minor issue, but its consequences can be severe, and many wonder, "can gum disease kill you?" When left untreated, it can lead to infections that spread beyond your mouth, affecting your entire body. Studies show that inflammation caused by gum disease increases the risk of heart disease, diabetes, and even life-threatening conditions like sepsis. Experts emphasize that poor oral health can trigger chronic inflammation, which damages tissues and organs over time. This connection highlights why maintaining oral hygiene is essential. By addressing gum disease early, you can reduce health risks and protect your overall well-being.
What Is Gum Disease?
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a common oral health condition that affects the tissues supporting your teeth. It begins with bacterial growth in your mouth and can progress to severe stages if left untreated. Understanding its types, causes, and symptoms can help you take proactive steps to protect your oral health.
Types of Gum Disease
Gingivitis: The Early Stage
Gingivitis is the mildest form of gum disease. It occurs when plaque, a sticky film of bacteria, builds up on your teeth and irritates your gums. You may notice red, swollen gums that bleed easily when brushing or flossing. Fortunately, gingivitis is reversible with proper oral hygiene and professional dental care. Ignoring these early signs of gum disease, however, can lead to more serious complications.
Periodontitis: Advanced Gum Disease
When gingivitis progresses, it can turn into periodontitis. This advanced stage causes permanent damage to the gums and bone supporting your teeth. Symptoms include gum recession, loose teeth, and painful chewing. Periodontitis not only threatens your oral health but also increases your risk of systemic conditions like heart disease and diabetes. Studies show that untreated periodontitis can even allow bacteria to enter your bloodstream, leading to severe infections.
How Gum Disease Develops
Plaque and Tartar Buildup
Plaque forms when bacteria in your mouth mix with food particles and saliva. If you don’t remove it through regular brushing and flossing, it hardens into tartar. Tartar is more difficult to remove and provides a breeding ground for harmful bacteria. This buildup irritates your gums, triggering inflammation and infection.
Inflammation and Infection
As bacteria attack your gum tissues, your body responds with inflammation. While this is a natural defense mechanism, chronic inflammation can destroy the structures that hold your teeth in place. Over time, the infection spreads deeper, causing further damage to your gums, bones, and connective tissues. Without treatment, this process can lead to tooth loss and other health complications.
Recognizing Symptoms of Gum Disease
Bleeding and Swollen Gums
One of the first signs of gum disease is bleeding gums, especially during brushing or flossing. Swollen, tender gums that appear red or purplish are also common indicators. These symptoms suggest that your gums are inflamed and need immediate attention.
Persistent Bad Breath and Gum Recession
Bad breath that doesn’t go away, even after brushing, could signal gum disease. As the condition worsens, you might notice your gums pulling away from your teeth, creating pockets where bacteria thrive. This gum recession not only affects your smile but also exposes your teeth to further damage.
Tip: Regular dental visits can help you spot the early signs of periodontal disease and prevent it from progressing.
Can Gum Disease Kill You?
Gum disease might not seem life-threatening at first glance, but its consequences can be far-reaching. When left untreated, it can lead to severe infections and systemic health risks that may increase the likelihood of death. Understanding these risks is essential to protect your health and well-being.
Severe Infections and Systemic Risks
Untreated Periodontitis and Sepsis
Untreated periodontitis can have devastating effects on your body. As the disease progresses, bacteria from your gums can enter your bloodstream. This process, known as bacteremia, allows harmful microbes to travel throughout your body. Studies have shown that this can compromise your immune system, making you more vulnerable to severe infections. In extreme cases, the bacteria can trigger sepsis, a life-threatening condition where your body’s response to infection causes widespread inflammation and organ failure. Without prompt treatment, sepsis can lead to death.
The connection between gum disease and systemic infections highlights the importance of early intervention. By addressing periodontitis before it worsens, you can prevent bacteria from spreading and reduce the risk of severe complications.
Chronic Inflammation and Organ Damage
Chronic inflammation caused by gum disease doesn’t just affect your mouth. It can have a ripple effect throughout your body. When your immune system responds to gum infections, it releases inflammatory markers into your bloodstream. Over time, this chronic inflammation can damage vital organs, including your heart, kidneys, and lungs. Research has linked this immune response to an increased risk of heart disease, diabetes, and even complications from COVID-19.
The long-term impact of chronic inflammation underscores the need for regular dental care. By managing gum disease effectively, you can protect your organs and maintain your overall health.
Long-Term Health Risks
Compounding Effects on Preexisting Conditions
Gum disease can worsen preexisting health conditions, creating a dangerous cycle. For example, if you have diabetes, gum disease can make it harder to control your blood sugar levels. This bidirectional relationship means that poor oral health can exacerbate diabetes, while uncontrolled diabetes can accelerate the progression of gum disease. Similarly, individuals with cardiovascular conditions face heightened risks, as inflammation from gum disease can contribute to atherosclerosis and increase the likelihood of heart attacks or strokes.
The compounding effects of gum disease on existing conditions highlight the importance of proactive care. By maintaining good oral hygiene and seeking timely treatment, you can minimize these risks and improve your quality of life.
Increased Mortality Risk from Systemic Diseases
Chronic gum disease has been associated with an increased risk of early death. Studies have found that individuals with advanced periodontitis face a higher likelihood of developing systemic diseases, including Alzheimer’s, respiratory infections, and even certain cancers. For instance, research published in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute revealed a 24% increase in cancer risk among individuals with severe periodontitis. The highest risks were observed for lung and colorectal cancers.
These findings emphasize the serious consequences of ignoring gum disease. By addressing the condition early, you can reduce your risk of life-threatening diseases and improve your chances of living a longer, healthier life.
The Systemic Health Risks of Gum Disease
Gum disease doesn’t just affect your mouth. It can lead to serious health complications throughout your body. From cardiovascular disease to pregnancy challenges, the systemic risks of untreated gum disease are significant. Understanding these risks can help you take proactive steps to protect your overall health.
Cardiovascular Complications
Inflammation and Atherosclerosis
Gum disease can directly impact your cardiovascular health. The bacteria responsible for gum infections can travel through your bloodstream, causing inflammation in your blood vessels. This inflammation can lead to the formation of tiny blood clots and fatty deposits, a condition known as atherosclerosis. Studies have found oral bacteria in these deposits, confirming a direct link between gum disease and cardiovascular disease. Atherosclerosis narrows your arteries, increasing the risk of heart attacks and strokes.
Increased Risk of Heart Attack and Stroke
The connection between gum disease and cardiovascular complications is alarming. Chronic inflammation caused by periodontal disease can weaken your heart’s blood vessels. This increases the likelihood of life-threatening events like heart attacks and strokes. Research supports this link, showing that untreated gum disease can significantly raise your risk of these conditions. By addressing gum disease early, you can reduce these risks and protect your heart health.
Diabetes and Blood Sugar Control
Bidirectional Relationship Between Gum Disease and Diabetes
The relationship between gum disease and diabetes goes both ways. If you have diabetes, you’re more likely to develop periodontal disease. This is because high blood sugar levels can weaken your immune system, making it harder for your body to fight infections. On the other hand, gum disease can make it more difficult to control your blood sugar levels. Studies have shown that treating periodontal disease can improve blood sugar management, highlighting the importance of oral health for those with diabetes.
Challenges in Managing Blood Sugar Levels
Gum disease can complicate diabetes management. Inflammation from gum infections can interfere with your body’s ability to use insulin effectively. This can lead to higher blood sugar levels, worsening your condition. Research has also found that patients with diabetes who receive periodontal treatment often experience a reduction in HbA1c levels, a key marker of blood sugar control. Maintaining good oral hygiene and seeking timely treatment can help you manage your diabetes more effectively.
Pregnancy Complications
Preterm Birth and Low Birth Weight
Gum disease can pose serious risks during pregnancy. Studies have linked periodontal disease to preterm birth and low birth weight. Harmful bacteria from infected gums can enter your bloodstream and reach the fetus, potentially causing complications. Inflammatory mediators released during gum infections can also trigger early labor or affect fetal development. These risks make it essential for pregnant women to prioritize oral health.
Hormonal Changes and Gum Health
Pregnancy hormones can increase your risk of developing gum disease. Hormonal changes make your gums more sensitive to plaque, leading to inflammation and gingivitis. This condition, known as pregnancy gingivitis, can progress to more severe periodontal disease if left untreated. Regular dental visits and proper oral hygiene can help you manage these changes and reduce the risk of complications.
Tip: If you’re pregnant, inform your dentist and schedule a checkup to address any gum health concerns.
Other Health Risks
Gum disease doesn’t just harm your mouth. It can lead to serious health complications in other parts of your body. These risks include respiratory infections, pneumonia, and even conditions like Alzheimer’s and cancer. Understanding these connections can help you take better care of your oral health and overall well-being.
Respiratory Infections and Pneumonia
Gum disease can increase your risk of respiratory infections. Bacteria from infected gums can travel through your bloodstream or enter your airways. Once in your lungs, these bacteria may cause inflammation, leading to conditions like pneumonia or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Studies show that periodontal pathogens can worsen lung health by triggering inflammatory responses in lung tissues. This makes it harder for your body to fight off infections.
If you already have a respiratory condition, gum disease can make it worse. The bacteria from your mouth can aggravate existing lung problems, increasing the severity of your symptoms. Regular dental care and good oral hygiene can reduce these risks. By keeping your gums healthy, you can protect your lungs and lower your chances of developing serious respiratory issues.
Note: If you experience breathing problems and have gum disease, consult your dentist and doctor. Early treatment can prevent complications.
Potential Links to Alzheimer’s and Cancer
Gum disease may also affect your brain. Research suggests a connection between periodontal disease and Alzheimer’s. Patients with Alzheimer’s who also have gum disease show higher levels of inflammatory markers like TNF-α. These markers indicate that gum infections may contribute to brain inflammation, increasing the risk of dementia. Poor oral hygiene can worsen this cycle, as Alzheimer’s patients often struggle to maintain their dental health.
The link between gum disease and cancer is another growing concern. Studies reveal that individuals with severe periodontitis face a higher risk of developing certain cancers, including lung and colorectal cancer. One study found that gum disease bacteria are associated with a 50% increased risk of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC). These findings highlight the importance of oral hygiene in reducing cancer risks.
Maintaining healthy gums can protect more than just your teeth. By preventing gum disease, you can lower your risk of life-threatening conditions like dementia and cancer. Regular dental visits and proper oral care are essential steps in safeguarding your overall health.
Tip: Brush and floss daily to remove plaque and bacteria that could harm your gums and increase your risk of systemic diseases.
Preventing Gum Disease
Preventing gum disease starts with adopting consistent oral hygiene habits and making healthy lifestyle choices. By taking proactive steps, you can protect your gums, teeth, and overall health from the harmful effects of gum disease.
Daily Oral Hygiene Practices
Proper Brushing and Flossing Techniques
Brushing and flossing are your first line of defense against gum disease. Brush your teeth twice daily using a soft-bristled toothbrush. Focus on cleaning along the gumline, where plaque tends to accumulate. Floss daily to remove food particles and plaque from between your teeth, areas your toothbrush cannot reach. Don’t forget to brush your tongue, as it harbors bacteria that can cause bad breath and contribute to gum infections.
Tip: Replace your toothbrush every three months or sooner if the bristles fray.
Choosing Effective Oral Care Products
The right oral care products can make a significant difference in maintaining excellent oral hygiene. Use a fluoride toothpaste to strengthen your teeth and prevent decay. Consider adding an antibacterial mouthwash to your routine to reduce plaque buildup and kill harmful bacteria. If you’re prone to gum issues, look for products specifically designed for gum health.
Note: Avoid tobacco products, as they increase your risk of gum disease and other oral health problems.
Regular Dental Visits
Professional Cleanings and Checkups
Regular dental visits are essential for preventing gum disease. Dentists recommend scheduling cleanings and checkups every six months. These visits allow your dentist to remove tartar, which cannot be eliminated through brushing alone. Professional cleanings also help prevent plaque from hardening and causing gum inflammation.
Early Detection of Gum Disease
Routine checkups enable your dentist to spot early signs of gum disease, such as gingivitis, before it progresses to more severe stages. Early detection ensures timely treatment, reducing the risk of complications like tooth loss or systemic infections. If you have a history of gum disease or other risk factors, your dentist may suggest more frequent visits.
Tip: Inform your dentist about any changes in your oral health, such as bleeding gums or persistent bad breath.
Healthy Lifestyle Choices
Balanced Diet and Nutrition
A balanced diet plays a crucial role in maintaining healthy gums. Foods rich in vitamins C and D support gum tissue repair and reduce inflammation. Incorporate leafy greens, citrus fruits, and dairy products into your meals to strengthen your gums and teeth. Avoid sugary snacks and drinks, as they promote plaque buildup and increase your risk of gum disease.
Avoiding Smoking and Excessive Alcohol
Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can severely impact your oral health. Smoking reduces blood flow to your gums, making it harder for them to heal and fight infections. Alcohol can dry out your mouth, creating an environment where bacteria thrive. By avoiding these habits, you can significantly lower your risk of developing gum disease.
Reminder: Small lifestyle changes, like drinking more water and eating nutrient-rich foods, can have a big impact on your gum health.
Managing Gum Disease
Managing gum disease effectively can prevent it from progressing to severe stages and causing irreversible damage. By understanding the available treatments and long-term strategies, you can protect your oral health and overall well-being.
Treating Gingivitis
Non-Surgical Interventions
Gingivitis, the earliest stage of gum disease, responds well to non-surgical treatments. Dentists often recommend professional cleanings to remove plaque and tartar buildup. This process eliminates the bacteria causing inflammation and allows your gums to heal. Maintaining proper oral hygiene at home is equally important. Brushing twice daily and flossing can prevent plaque from reforming.
For mild cases, dentists may suggest lifestyle changes to reduce risk factors. Quitting smoking and improving your diet can strengthen your gums and reduce inflammation. These simple steps can stop gingivitis from advancing to periodontitis, a more severe condition.
Antibacterial Mouthwashes and Rinses
Antibacterial mouthwashes play a key role in treating gingivitis. These rinses target harmful bacteria, reducing inflammation and bad breath. Dentists often recommend chlorhexidine-based mouthwashes for their effectiveness in controlling bacterial growth. Using these products as part of your daily routine can enhance your oral hygiene and support gum health.
Treatment | Description |
|---|---|
Scaling and root planing | A deep cleaning procedure that removes tartar and bacteria, smoothing tooth roots to prevent bacteria from adhering. |
Improved oral hygiene | Maintaining cleanliness through proper dental care and regular checkups to prevent recurrence. |
Antimicrobial mouthwash | Rinsing with this type of mouthwash helps eliminate harmful bacteria that cause gingivitis. |
Addressing Periodontitis
Scaling and Root Planing
Scaling and root planing is the cornerstone of periodontitis treatment. This deep cleaning procedure removes tartar and bacteria from below the gumline. It also smooths the tooth roots, making it harder for bacteria to reattach. Advanced techniques, such as laser-assisted periodontal therapy, offer minimally invasive options. These methods remove infected tissues and promote faster healing.
Recent advancements, like guided tissue regeneration and platelet-rich plasma therapy, have improved outcomes. These techniques stimulate the regrowth of damaged bone and gum tissue. Studies show that combining scaling and root planing with systemic antibiotics enhances results. Patients experience reduced probing depths and improved gum attachment levels.
Surgical Options for Severe Cases
Severe periodontitis may require surgical intervention. Procedures like flap surgery allow dentists to clean deep pockets and reshape the underlying bone. Gum grafting can cover exposed roots, protecting them from decay and improving aesthetics.
Surgical Procedure | Description |
|---|---|
Osseous Surgery | Reshapes the bone around teeth and reduces gum pockets by eliminating bacteria. |
Pocket Reduction Surgery | Involves incisions along the gum line to clean below the tissue and reduce pocket depth. |
Gum Grafting | Transplants gum tissue to cover exposed tooth roots, protecting them from decay and enhancing aesthetics. |
Flap Surgery | Allows thorough cleaning of deep pockets and reshaping of underlying bone for optimal gum reattachment. |
Bone Grafting | Restores damaged bone using the patient's own bone or synthetic materials to stabilize teeth. |
Long-Term Maintenance
Periodontal Maintenance Therapy
After treatment, maintaining gum health is crucial. Periodontal maintenance therapy involves regular cleanings and checkups to monitor your progress. Dentists focus on removing plaque and tartar to prevent recurrence. This ongoing care ensures that your gums remain healthy and free from infection.
Monitoring for Recurrence
Staying vigilant for signs of gum disease is essential. Watch for symptoms like bleeding gums or persistent bad breath. Regular dental visits help detect any issues early. A balanced diet and proper oral hygiene further support long-term gum health.
Schedule regular follow-up appointments with your dentist or periodontist to monitor gum health.
Continue to brush and floss regularly, paying attention to the gumline.
Undergo professional dental cleanings to remove hardened plaque.
Be vigilant for signs of gum disease, such as bleeding gums or persistent bad breath.
Maintain a healthy lifestyle by eating a balanced diet and avoiding excessive sugar intake.
Periodontal maintenance prevents complications and protects your teeth and gums. By following these steps, you can reduce the risk of recurrence and enjoy better oral health.
The Future of Gum Disease Prevention and Treatment
The future of gum disease prevention and treatment looks promising with advancements in technology and increased public awareness. These innovations aim to make early detection and treatment more effective while reducing the burden of periodontal disease on overall health.
Innovations in Dental Technology
AI Tools for Early Detection
Artificial intelligence (AI) is transforming how dentists diagnose and monitor gum disease. AI-powered tools analyze dental images to identify early signs of inflammation or bone loss. These systems can track changes in your gum health over time, helping your dentist detect problems before they worsen. Some AI tools even integrate with wearable devices, allowing continuous monitoring of your oral health. This technology can predict your risk of developing gum disease by analyzing genetic factors and oral hygiene habits. Early diagnosis through AI improves treatment outcomes and enhances your quality of life.
Studies show that AI systems, such as deep neural networks, accurately measure periodontal bone loss. These tools provide precise insights, enabling dentists to create tailored treatment plans. By adopting AI, dental care becomes more proactive, reducing the chances of severe complications.
Minimally Invasive Treatment Options
Minimally invasive treatments are revolutionizing how gum disease is managed. Laser therapy removes diseased tissue and bacteria without the discomfort of traditional methods. This approach targets specific areas, ensuring faster recovery and less pain. Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) therapy uses your blood to promote healing and regenerate gum tissue. It offers a natural and effective solution with minimal risk of infection.
Other innovations include Piezoelectric Ultrasonic Scaling, which provides precise cleaning, and Photodynamic Therapy (PDT), which eliminates harmful bacteria. These advancements make treatments more comfortable and accessible, encouraging you to seek care earlier.
Treatment Option | Description | Advantages |
|---|---|---|
Laser Therapy | A non-invasive procedure using a laser to remove diseased tissue and bacteria. | Less discomfort, shorter recovery time, and more precise targeting of specific gum areas. |
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) | Uses a patient's own blood to promote healing and regeneration of gum tissue. | Natural treatment with low risk of infection, effective healing, quicker recovery, and better outcomes. |
Public Awareness and Education
Campaigns Promoting Oral Health
Public health campaigns play a vital role in reducing gum disease prevalence. For example, Japan’s 8020 Campaign encourages people to maintain at least 20 teeth by age 80. This initiative highlights the importance of oral hygiene and behavior changes. Over time, such campaigns have significantly improved oral health awareness.
Year | Knowledge of Tooth Brushing (%) | Daily Flossing Prevalence (%) |
|---|---|---|
1982 | 31.7 | 20.1 |
1983 | 37.9 | 24.9 |
These efforts demonstrate how education can lead to better habits and healthier gums. By participating in similar programs, you can learn effective ways to prevent gum disease and protect your overall health.
Integrating Dental and Medical Care
Integrating dental and medical care addresses the systemic risks of gum disease. Collaboration between dentists and doctors ensures comprehensive care. For instance, dental screenings for chronic diseases like diabetes can become part of routine medical checkups. This approach helps identify health issues early and improves treatment outcomes.
However, challenges remain. Many healthcare systems lack integrated electronic health records, making it difficult for providers to share information. Training programs for healthcare workers often overlook the connection between oral and systemic health. Addressing these gaps can enhance care quality and reduce health disparities.
Challenge | Description |
|---|---|
Lack of communication and coordination | Medical and dental practices often do not communicate effectively, leading to fragmented care. |
Absence of integrated electronic health records | Without integrated HER, providers cannot access a unified care plan for patients. |
Insufficient training programs | Healthcare workers lack training in integrated care approaches. |
Health gaps | There are disparities in health access and outcomes between urban and rural areas. |
Lack of oral health policies | Insufficient policies contribute to the perception of oral health as non-urgent. |
By integrating dental and medical care, you can benefit from a more holistic approach to health management. This collaboration ensures that your oral health receives the attention it deserves.
Gum disease may not directly kill you, but its consequences can severely impact your health. Untreated gum infections can spread through your bloodstream, increasing the risk of life-threatening conditions like heart disease, strokes, and sepsis. Early detection and proper treatment prevent these complications. Regular dental visits and consistent oral hygiene protect your gums and reduce the chances of developing advanced periodontal disease. By addressing gum health proactively, you safeguard your overall well-being and avoid the irreversible damage caused by this common condition.
Remember: Healthy gums support a healthier life. Take action today to prevent gum disease from affecting your future.
FAQ
Can gum disease kill you?
Gum disease itself doesn’t directly kill you, but it can lead to severe health complications. Untreated periodontitis allows bacteria to enter your bloodstream, increasing the risk of heart disease, strokes, and even sepsis. These conditions can become life-threatening if ignored.
How can gum disease affect your overall health?
Gum disease causes chronic inflammation, which spreads through your body. This inflammation increases your risk of systemic diseases like diabetes, cardiovascular issues, and respiratory infections. Studies link untreated gum infections to organ damage and other serious health problems.
Can a gum infection kill you if left untreated?
Yes, untreated gum infections can lead to sepsis, a deadly condition where your body’s response to infection causes widespread inflammation. This can result in organ failure or death. Early treatment prevents bacteria from spreading and reduces this risk.
What are the early signs of gum disease?
Early signs include red, swollen gums that bleed during brushing or flossing. Persistent bad breath, gum recession, and plaque buildup are also common. Recognizing these symptoms early helps you prevent progression to severe stages like periodontitis.
Can periodontitis kill you?
Periodontitis can indirectly kill you by increasing your risk of fatal conditions. Bacteria from infected gums can travel through your bloodstream, causing heart attacks, strokes, or systemic infections. Proper dental care reduces these life-threatening risks.
How long does it take for gum disease to become severe?
Gum disease progresses at different rates depending on your oral hygiene and health. Gingivitis, the mild stage, can develop within weeks. If untreated, it may progress to periodontitis over months or years, causing irreversible damage.
Can bleeding gums kill you?
Bleeding gums alone won’t kill you, but they signal gum disease. If ignored, the condition can worsen, leading to systemic infections or chronic diseases. Address bleeding gums early to avoid severe health complications.
How do you kill periodontal bacteria?
You can kill periodontal bacteria by maintaining proper oral hygiene. Brush twice daily, floss regularly, and use antibacterial mouthwash. Professional dental cleanings remove tartar and bacteria from hard-to-reach areas, preventing infections from spreading.
Tip: Regular dental visits and early intervention are key to managing gum disease and protecting your health.
See Also
Identifying Signs That Gum Disease May Be Present
Exploring Gum Issues and Their Impact on Pregnancy
Uncovering Risks of Gum Issues in Expecting Mothers
