Can wisdom teeth cause gingivitis? Here's why
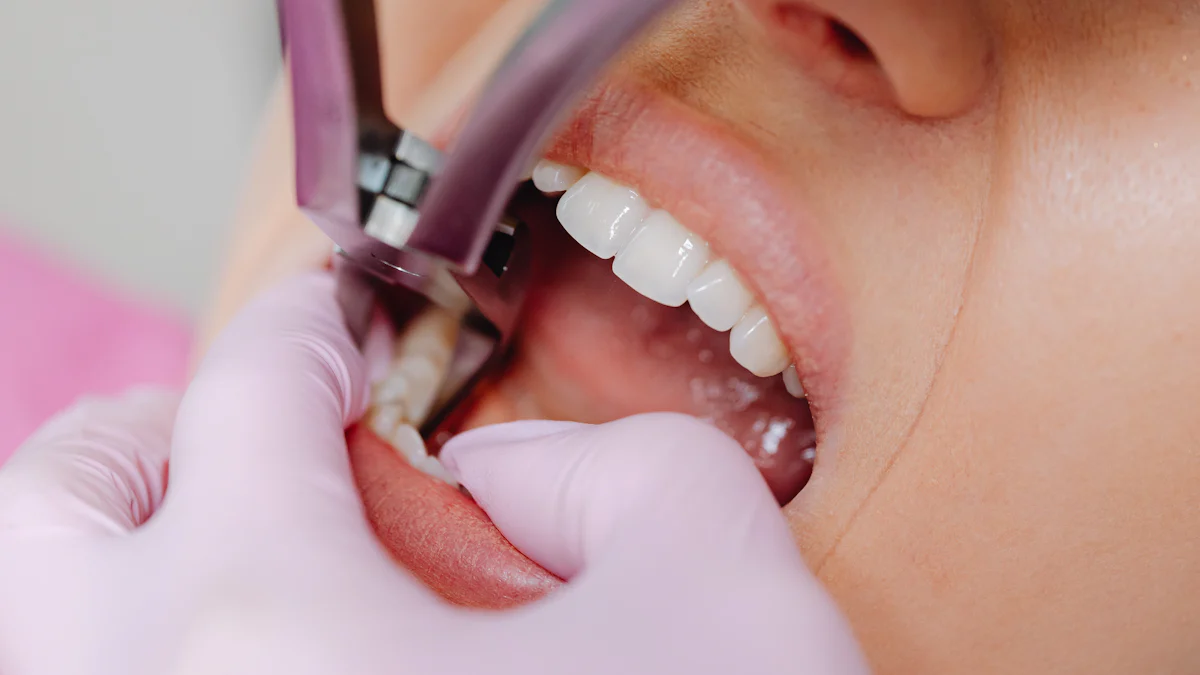
Wisdom teeth often pose challenges to your oral health. Their location at the back of your mouth makes them difficult to clean, which raises the question: can wisdom teeth cause gingivitis? The buildup of bacteria and plaque around these teeth can indeed lead to gum inflammation, commonly known as gingivitis. Research indicates that 60% of young adults with wisdom teeth experience early signs of gum disease, with 25% seeing their condition worsen over time. Partially erupted or impacted wisdom teeth further heighten the risk of gum problems by trapping food and bacteria. If these issues are not addressed, they can progress, resulting in pain, swelling, and even infection.
Why can wisdom teeth cause gingivitis?
Wisdom teeth can create unique challenges for your oral health. Their position and growth patterns often lead to issues that increase the risk of gingivitis. Understanding these factors can help you take proactive steps to protect your gums and overall dental health.
Difficulty in cleaning wisdom teeth
Cleaning wisdom teeth can be tricky due to their location at the back of your mouth. This area is hard to reach with a toothbrush or floss, making it easy for food particles to get trapped. If your wisdom teeth are only partially erupted, the situation becomes even more complicated. The surrounding gum tissue may form a flap, creating a space where bacteria and plaque can accumulate. Over time, this buildup can lead to cavities, gum irritation, and even periodontal disease. You might notice swelling, tenderness, or difficulty keeping the area clean, all of which increase the risk of gingivitis.
Bacteria and plaque buildup
Plaque buildup is a common issue around wisdom teeth. When you cannot clean these teeth properly, bacteria thrive in the hard-to-reach areas. Plaque, a sticky film of bacteria, forms on the surface of your teeth and along the gumline. If left untreated, it hardens into tartar, which irritates the gums and causes inflammation. This process can lead to gingivitis, with symptoms like redness, swelling, and bleeding gums. The bacteria in plaque also release toxins that attack the gum tissue, worsening the condition over time. Regular brushing and flossing are essential, but wisdom teeth often make these tasks more challenging.
Gum pockets and inflammation
Wisdom teeth can cause gum pockets to develop, especially if they erupt at an angle or remain partially erupted. These pockets create a space where bacteria and food debris can lodge, leading to infection and inflammation. The inflamed gum tissue becomes swollen and painful, making it even harder to clean the area effectively. Over time, these pockets can deepen, increasing the risk of gum disease and tooth loss. You may also experience bad breath, a bad taste in your mouth, or persistent discomfort. Addressing these issues early can prevent more severe complications.
Impacted or partially erupted wisdom teeth
Impacted or partially erupted wisdom teeth can significantly affect your oral health. These teeth often fail to emerge fully due to a lack of space in your jaw or because they grow at an angle. When this happens, they can create a host of problems, including gingivitis and other gum-related issues.
Impacted wisdom teeth remain trapped beneath the gum tissue or within the jawbone. This condition can lead to pain, swelling, and even infections. The surrounding gums may become inflamed, red, and tender, making it difficult for you to clean the area properly. Bacteria and food particles often get trapped around these teeth, causing plaque buildup. Over time, this can lead to gum disease, cavities, and even more severe conditions like pericoronitis—a painful infection of the gum tissue around a partially erupted tooth.
Partially erupted wisdom teeth, on the other hand, break through the gumline but do not fully emerge. This creates a flap of gum tissue that can trap debris and bacteria. The trapped particles can irritate the gums, leading to inflammation and infection. You might notice symptoms like bad breath, a bad taste in your mouth, or gums that bleed when you brush. These signs indicate that the area is not being cleaned effectively, increasing the risk of developing gingivitis.
The pressure from impacted wisdom teeth can also cause overcrowding in your mouth. This can push neighboring teeth out of alignment, creating additional spaces where plaque and bacteria can accumulate. Overcrowding not only affects the appearance of your smile but also makes it harder to maintain proper oral hygiene. In some cases, impacted wisdom teeth can even damage the roots of nearby teeth or the jawbone itself, leading to more complex dental issues.
If you experience persistent discomfort, swelling, or signs of infection around your wisdom teeth, you should consult a dentist. Early treatment can prevent these problems from worsening. Dentists often recommend wisdom tooth removal to eliminate the source of irritation and reduce the risk of gum disease. Regular dental checkups and professional cleanings can also help you manage the challenges posed by impacted or partially erupted wisdom teeth.
Ignoring these issues can lead to severe complications, including periodontal disease and tooth loss. By addressing the problem early, you can protect your gums and maintain your overall oral health.
Symptoms of gingivitis caused by wisdom teeth
Gingivitis caused by wisdom teeth often presents unique symptoms due to their location and growth patterns. Recognizing these signs early can help you take action to prevent further complications. Below are the common symptoms and those specifically linked to wisdom teeth, along with guidance on when to seek professional help.
Common signs of gingivitis
Gingivitis typically starts with mild symptoms that can worsen over time if left untreated. You may notice your gums becoming red, swollen, or tender. Bleeding gums, especially when brushing or flossing, is another common sign. Bad breath or a persistent bad taste in your mouth often accompanies these symptoms.
Plaque buildup plays a significant role in causing these issues. When plaque accumulates along the gumline, it irritates the soft tissue, leading to inflammation. Over time, this can result in gum pockets, where bacteria and food particles get trapped. These pockets make it even harder to clean your teeth properly, increasing the risk of gum disease.
Symptoms specific to wisdom teeth
Wisdom teeth can cause unique symptoms of gingivitis due to their position and eruption process. If your wisdom teeth are partially erupted, you might notice a flap of gum tissue covering part of the tooth. This flap can trap food and bacteria, leading to localized swelling and irritation.
Impacted wisdom teeth, which fail to fully emerge, can cause pressure and pain in the surrounding gums and jaw. You may experience swelling near the back of your mouth, difficulty opening your jaw, or even headaches. In some cases, the gums around wisdom teeth may bleed more easily or feel especially tender when touched.
Another symptom to watch for is pericoronitis, a painful infection that occurs around partially erupted wisdom teeth. This condition can cause severe discomfort, bad breath, and even difficulty swallowing. If you notice these symptoms, it’s essential to address them promptly to avoid further complications.
When to seek professional help
You should consult a dentist if you experience persistent symptoms of gingivitis, especially those linked to wisdom teeth. Signs like severe swelling, intense pain, or difficulty chewing indicate that the problem may require professional treatment.
If you notice pus around your gums, a foul taste in your mouth, or signs of infection, seek immediate care. These symptoms could signal advanced gum disease or an abscess, which can spread to other areas if untreated.
Regular dental checkups can help you monitor the health of your wisdom teeth and gums. Dentists can identify early signs of gingivitis and recommend appropriate treatment, such as professional cleaning or wisdom tooth removal. Acting early can prevent more severe issues, like periodontal disease or tooth loss.
How to prevent gum disease from wisdom teeth
Preventing gum disease caused by wisdom teeth requires consistent care and attention. By adopting effective oral hygiene practices, scheduling regular dental visits, and making healthy lifestyle choices, you can reduce the risk of developing gingivitis or other gum-related issues.
Maintaining proper oral hygiene
Proper oral hygiene is your first line of defense against gum disease. Wisdom teeth, due to their position, can be challenging to clean. However, following a thorough cleaning routine can help you maintain healthy gums.
Brush your teeth at least twice daily using fluoride toothpaste. Fluoride strengthens enamel and protects against decay.
Floss daily to remove plaque and food particles from between your teeth.
Consider using an oral irrigator to clean around the gumline, especially near wisdom teeth.
Choose a toothbrush that suits your needs. Electric toothbrushes can provide more effective cleaning for hard-to-reach areas.
Brush after meals whenever possible to prevent plaque buildup.
Incorporating these habits into your daily routine ensures that bacteria and debris do not accumulate around your wisdom teeth, reducing the chance of gum inflammation.
Regular dental checkups
Regular dental visits play a crucial role in preventing gum disease. Dentists can monitor the health of your wisdom teeth and gums, identifying potential problems early.
Schedule dental checkups at least twice a year for professional cleanings and examinations.
If you are at higher risk for gum disease, such as if you smoke or have diabetes, visit your dentist every three to four months.
During these visits, your dentist can remove tartar, which cannot be eliminated through brushing alone.
Professional cleanings and early intervention can prevent minor issues from escalating into severe gum disease or infections.
Healthy diet and lifestyle choices
Your diet and lifestyle significantly impact your oral health. Making mindful choices can strengthen your gums and teeth while reducing the risk of gum disease.
Eat a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. These foods provide essential nutrients for gum health.
Limit sugary snacks and beverages, as they contribute to plaque formation.
Stay hydrated to promote saliva production, which helps wash away food particles and bacteria.
Avoid smoking, as it weakens your immune system and increases the risk of gum disease.
By maintaining a healthy lifestyle, you support your body’s natural ability to fight off infections and keep your gums in optimal condition.
Treatment options for gingivitis caused by wisdom teeth
Treating gingivitis caused by wisdom teeth involves addressing the root of the problem. Depending on the severity of your symptoms, you may need professional dental care, wisdom tooth extraction, or home remedies to manage the condition effectively.
Professional dental treatments
Professional dental treatments are often the first step in managing gingivitis caused by wisdom teeth. Dentists use specialized tools to clean areas that are difficult for you to reach. This process removes plaque and tartar buildup, reducing inflammation and irritation around your gums.
Your dentist may recommend scaling and root planing if the gingivitis has progressed. This deep cleaning procedure targets bacteria below the gumline, smoothing the tooth roots to prevent further plaque accumulation. In some cases, antibiotics may be prescribed to control infection and promote healing.
Regular dental visits are essential for monitoring your oral health. Professional cleanings not only treat existing issues but also help prevent future problems. If your wisdom teeth are causing persistent gum disease, your dentist might suggest further interventions, such as extraction.
Wisdom tooth extraction
Wisdom tooth extraction is a common solution for gingivitis caused by impacted or partially erupted teeth. Removing these teeth eliminates the bacteria-prone areas where food and plaque tend to get trapped. This reduces the risk of gum disease and prevents complications like gum pockets or receding gums.
Benefits of wisdom tooth extraction include:
Reducing the risk of infections, cysts, and abscesses.
Preventing inflammation and gum tissue damage.
Avoiding overcrowding and pressure on neighboring teeth.
However, extraction is not without risks. You may experience temporary discomfort or swelling after the procedure. In rare cases, complications like nerve damage or dry socket can occur. Dry socket, a painful condition where the blood clot dislodges from the extraction site, can delay healing.
Your dentist will evaluate your situation to determine if extraction is necessary. For many patients, removing wisdom teeth provides long-term relief from gum-related issues and improves overall oral health.
Home remedies and self-care
Home remedies and self-care can complement professional treatments and help you manage mild symptoms of gingivitis. Maintaining a consistent oral hygiene routine is crucial. Brush your teeth twice daily and floss to remove plaque from hard-to-reach areas. Using an antibacterial mouthwash can also reduce bacteria and freshen your breath.
Saltwater rinses are a simple yet effective remedy for soothing inflamed gums. Dissolve half a teaspoon of salt in warm water and rinse your mouth gently. This helps reduce swelling and promotes healing.
Applying a cold compress to the outside of your jaw can alleviate pain and swelling caused by wisdom teeth. Over-the-counter pain relievers may also provide temporary relief. However, these remedies should not replace professional care if your symptoms persist or worsen.
By combining self-care with professional treatments, you can effectively manage gingivitis and protect your gums from further damage.
Risks of ignoring wisdom teeth-related gum disease
Ignoring gum disease caused by wisdom teeth can lead to serious oral health problems. What starts as mild inflammation or bleeding gums can quickly escalate into more severe conditions. Understanding these risks can help you take timely action to protect your teeth and gums.
Progression to severe gum disease
When you overlook gum disease, it doesn’t stay the same—it worsens over time. Gingivitis, the early stage of gum disease, begins with red, swollen gums that may bleed when you brush or floss. If untreated, it can progress to periodontitis, a more advanced condition that damages the tissue and bone supporting your teeth.
Periodontitis weakens the structural integrity of your teeth. This can lead to gum recession, where the gums pull away from the teeth, exposing the roots. Over time, the damage can cause your teeth to loosen or even fall out. Wisdom teeth, especially if impacted or partially erupted, increase the risk of this progression. Their position makes them harder to clean, allowing bacteria and plaque to thrive.
Did you know? Gum disease caused by wisdom teeth can also create complications like infections or cysts. These issues can damage the surrounding teeth and jawbone, making treatment more complex.
Here’s what can happen if gum disease progresses:
Tooth decay becomes more likely as cleaning wisdom teeth remains difficult.
Impacted wisdom teeth can create pressure, damaging neighboring teeth.
Infections may develop, causing pain and swelling that disrupt daily activities.
Ignoring these signs can lead to long-term consequences. Regular dental checkups and proper oral hygiene can prevent these issues from escalating.
Impact on overall health
Gum disease doesn’t just affect your mouth—it can impact your entire body. Inflammation caused by gum disease has been linked to several systemic health problems. For example, bacteria from infected gums can enter your bloodstream, increasing your risk of heart disease. Studies show that gum disease can raise cholesterol and fats in your blood, harming your cardiovascular system.
If you have diabetes, gum disease can make it harder to control your blood sugar levels. High glucose levels in saliva promote bacterial growth, worsening infections. This creates a cycle where gum disease and diabetes feed into each other, making both conditions harder to manage.
Health Tip: Treating gum disease early can reduce your risk of complications like heart disease and diabetes.
Other health issues associated with gum disease include:
Rheumatoid arthritis: Chronic inflammation from gum disease may worsen joint pain.
Alzheimer’s disease: Some studies suggest a link between oral bacteria and cognitive decline.
Pregnancy complications: Gum disease can increase the risk of preterm birth or low birth weight.
By addressing gum disease caused by wisdom teeth, you protect not only your oral health but also your overall well-being. Don’t wait for symptoms to worsen—consult your dentist at the first sign of trouble.
When to consult a dentist about wisdom teeth
Wisdom teeth can cause a variety of oral health issues, from mild discomfort to severe gum disease. Knowing when to consult a dentist is crucial for preventing complications and maintaining your dental health. Recognizing early warning signs and advanced symptoms can help you take timely action.
Early warning signs
Early signs of trouble with wisdom teeth often appear as mild discomfort or irritation. These symptoms may seem minor at first, but they can quickly worsen if ignored. Pay attention to the following signs that indicate it’s time to see a dentist:
Persistent pain or discomfort in the back of your mouth.
Swelling or redness around your gums.
Difficulty opening your mouth fully or chewing food.
Changes in your bite or jaw alignment.
Gums that bleed or feel tender when touched.
Visible crowding of your teeth as wisdom teeth push against them.
Bad breath or a foul taste in your mouth that doesn’t go away.
These symptoms often occur because wisdom teeth grow in awkward positions or fail to erupt properly. Food and bacteria can get trapped around these teeth, causing inflammation and irritation. If you notice any of these signs, don’t wait for the problem to escalate. Early intervention can save you from more serious dental issues.
Advanced symptoms of gum disease
When wisdom teeth-related problems go untreated, they can lead to advanced gum disease. This stage requires immediate attention to prevent permanent damage. Watch for these severe symptoms:
Loose teeth, which may indicate significant bone and tissue loss.
Teeth that shift position, creating gaps or misalignment.
Persistent swelling or pus around the gums, signaling an infection.
Severe pain that disrupts daily activities.
Increased sinus pressure or headaches caused by impacted wisdom teeth.
Advanced gum disease, also called periodontitis, can weaken the structures supporting your teeth. This condition may lead to tooth loss or infections that spread to other parts of your body. If you experience any of these symptoms, consult a dentist immediately for evaluation and treatment.
Importance of regular monitoring
Regular dental checkups are essential for keeping your wisdom teeth and gums healthy. Even if you don’t notice any symptoms, your dentist can identify potential problems before they become serious.
Tip: Schedule dental visits every six months, or more frequently if your dentist recommends it.
During these visits, your dentist will examine your wisdom teeth for signs of decay, infection, or improper growth. X-rays can reveal impacted teeth or other hidden issues. Regular monitoring ensures that any problems are addressed early, reducing the risk of complications like gum disease or tooth loss.
By staying proactive and consulting your dentist at the first sign of trouble, you can protect your oral health and avoid unnecessary pain or discomfort.
Wisdom teeth often create challenges for maintaining oral health. Their location and cleaning difficulties can lead to gingivitis and gum disease. Recognizing symptoms early, such as swollen gums or bleeding, allows you to take preventive steps. Practicing good oral hygiene, like brushing and flossing regularly, reduces the risk of plaque buildup. Regular dental visits are essential for monitoring wisdom teeth and addressing issues before they worsen. Dentists can detect problems like impacted teeth or infections early, ensuring timely treatment. If you suspect your wisdom teeth are causing discomfort or gum problems, consult your dentist for guidance. Addressing these issues promptly protects your oral health and prevents long-term complications.
FAQ
Can wisdom teeth cause gingivitis?
Yes, wisdom teeth can cause gingivitis. Their position makes cleaning difficult, leading to plaque buildup. This can irritate the gums, causing redness, swelling, and bleeding. Partially erupted or impacted wisdom teeth increase the risk by trapping food and bacteria, which worsens gum inflammation.
Do wisdom teeth cause gums to bleed?
Wisdom teeth can cause gums to bleed, especially if plaque and bacteria accumulate around them. Bleeding often occurs when brushing or flossing near the affected area. This is a common sign of gingivitis and should prompt you to consult a dentist for evaluation and treatment.
Can wisdom teeth cause gums to swell?
Yes, wisdom teeth can cause gums to swell. Swelling occurs due to trapped food, bacteria, or infection around partially erupted or impacted teeth. Inflamed gum tissue may feel tender or painful, making it harder to clean the area properly, which increases the risk of gum disease.
Can wisdom teeth lead to gum disease?
Wisdom teeth can lead to gum disease if not properly cleaned. Plaque and tartar buildup around these teeth irritates the gums, causing gingivitis. If untreated, this can progress to periodontitis, a severe gum disease that damages the bone and tissue supporting your teeth.
When should you see a dentist about wisdom teeth?
You should see a dentist if you experience persistent pain, swelling, or bleeding near your wisdom teeth. Signs like bad breath, difficulty chewing, or pus around the gums indicate infection or advanced gum disease. Early intervention prevents complications and protects your oral health.
Can wisdom teeth cause gums to recede?
Yes, wisdom teeth can cause gums to recede. Impacted or partially erupted teeth create pockets where bacteria thrive, leading to gum inflammation and tissue damage. Over time, this can cause the gums to pull away from the teeth, exposing the roots and increasing the risk of tooth loss.
How can you prevent gingivitis from wisdom teeth?
You can prevent gingivitis by maintaining proper oral hygiene. Brush and floss daily, use an antibacterial mouthwash, and schedule regular dental checkups. Professional cleanings remove plaque and tartar, reducing the risk of gum disease. Early removal of problematic wisdom teeth may also help.
Can wisdom teeth cause headaches or jaw pain?
Yes, wisdom teeth can cause headaches or jaw pain. Impacted teeth exert pressure on surrounding structures, leading to discomfort. This pain may radiate to your head or neck. If you notice these symptoms, consult a dentist to determine if your wisdom teeth are the cause.
See Also
The Impact Of Stress On Gum Disease And Oral Health
Exploring The Deadly Risks Of Periodontitis In Depth
The Life-Threatening Consequences Of Gum Disease Explained
