Connective Tissue Graft vs Free Gingival Graft: Which is Better for Gum Health
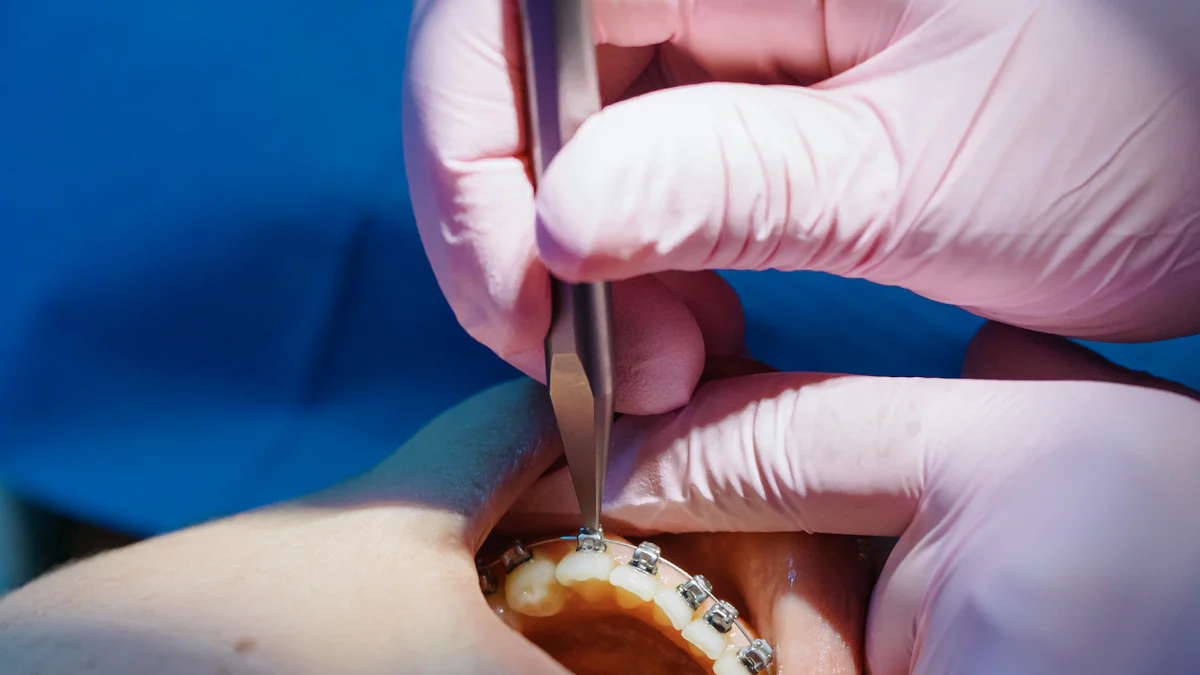
Gum grafting might seem daunting, but it’s a routine procedure that can significantly improve your oral health. If you’re experiencing receding gums, exposed tooth roots, or thin gum tissue, you’ve likely come across the terms connective tissue graft vs free gingival graft. These two grafting techniques are designed to address specific gum concerns and provide distinct advantages. A connective tissue graft is typically used to thicken your gums and enhance coverage, while a free gingival graft is aimed at increasing gum tissue in areas where it’s insufficient. Whether your goal is to treat gum disease, repair damage, or improve your smile, the choice between a connective tissue graft vs free gingival graft depends on your individual needs.
Fun fact: Gum grafting not only safeguards your teeth but also helps prevent sensitivity, decay, and even bone loss.
Deciding on a connective tissue graft vs free gingival graft may feel overwhelming, but understanding their unique purposes and benefits can empower you to make the best decision alongside your dentist.
Connective Tissue Graft
If you’re dealing with receding gums or exposed roots, a connective tissue graft might be the solution you need. This procedure is one of the most common and effective gum grafting techniques. It’s designed to improve gum thickness and provide better root coverage, helping to protect your teeth and enhance your smile.
What Is a Connective Tissue Graft?
A connective tissue graft involves taking a small piece of tissue from the roof of your mouth (the palate) and placing it over the affected area. Dentists typically use this method to treat gum recession and cover exposed roots. The tissue is carefully removed from beneath the top layer of the palate, leaving the outer layer intact. This technique minimizes discomfort and speeds up healing.
The graft is then secured to the receding gum area, where it integrates with the surrounding tissue. Over time, it strengthens the gums and provides additional coverage for exposed roots. This procedure is highly predictable and offers long-lasting results.
Benefits of Connective Tissue Grafts
You might wonder why this procedure is so popular. Here are some of the most significant benefits:
Protects exposed tooth roots from decay and damage.
Encourages the growth of healthy gum tissue, improving overall gum health.
Reduces sensitivity of exposed roots to temperature changes.
Repairs damage caused by gum recession and prevents further complications.
Enhances the appearance of your smile by restoring gum coverage.
Clinical studies back up these benefits. For example, one study reported an average root coverage of 98.4% after 27.5 months, with a failure rate of less than 2%. This high success rate makes connective tissue grafts a reliable option for treating gum recession.
Evidence Type | Success Rate | Failure Rate |
|---|---|---|
Average root coverage after CTG | 98.4% | < 2% |
When Is a Connective Tissue Graft Recommended?
Your dentist might recommend a connective tissue graft if you have advanced gingival recession or exposed roots that need protection. This procedure is ideal for patients with thin or inadequate gum tissue, as it helps to thicken the gums and provide better root coverage.
It’s also a great option if you’re experiencing sensitivity due to exposed roots or if you want to improve the cosmetic appearance of your smile. Dentists often choose this method because it offers predictable results and long-term benefits.
If you’re comparing connective tissue graft vs free gingival graft, the choice depends on your specific needs. While both procedures address gum issues, connective tissue grafts are particularly effective for treating advanced gingival recession and achieving excellent root coverage.
Healing and Recovery After a Connective Tissue Graft
Recovering from a connective tissue graft doesn’t have to feel overwhelming. With proper care and patience, you can expect a smooth healing process and long-lasting results. This procedure involves taking tissue from the roof of your mouth and grafting it to areas with gum recession. While the surgery itself is straightforward, understanding what to expect during recovery can help you feel more prepared.
Soft tissue healing typically takes about 4-8 weeks. Most patients notice significant improvement within the first month, but full recovery may take up to eight weeks. The healing time depends on factors like the amount of tissue removed and whether bone exposure occurred during the procedure. By the end of this period, the grafted tissue integrates with your gums, providing better coverage and protection for exposed roots.
Tip: Stick to soft foods like yogurt, mashed potatoes, or smoothies during the first week. Avoid anything crunchy or spicy to prevent irritation.
What to Expect During Recovery
After the surgery, you might experience mild discomfort or swelling around the graft and donor sites. This is completely normal and usually subsides within a few days. Your dentist will likely prescribe pain relievers or recommend over-the-counter options to keep you comfortable.
It’s essential to follow your dentist’s post-operative instructions closely. These may include:
Using a special mouth rinse to keep the surgical area clean.
Avoiding brushing or flossing near the graft site for the first week.
Scheduling follow-up visits to monitor your progress.
Common Complications
While connective tissue grafts are highly successful, complications can occasionally arise. Knowing what to watch for can help you address issues early. Some common complications include:
Severe swelling or loosening of sutures.
Tissue sloughing from the donor site.
Infection or uneven healing.
In rare cases, you might experience bleeding, gum graft failure, or prolonged swelling. If you notice any of these symptoms, contact your dentist immediately. Early intervention can prevent further complications and ensure a successful outcome.
Tips for a Faster Recovery
You play a major role in how quickly and smoothly you heal. Here are some tips to speed up recovery:
Rest as much as possible during the first few days.
Stick to a soft diet to avoid irritating the graft site.
Avoid smoking or drinking alcohol, as these can delay healing.
Follow all post-operative care instructions from your dentist.
By taking these steps, you can reduce discomfort and help your gums heal faster. A connective tissue graft not only restores gum health but also protects your teeth from further damage. With proper care, the results can last a lifetime.
Note: If you’re comparing a free gingival graft vs connective tissue graft, recovery times and comfort levels may differ. Connective tissue grafts are often considered less painful due to the subepithelial technique, which leaves the outer layer of the palate intact.
Free Gingival Graft
A free gingival graft is another effective option for gum grafting. If your gums are thin or receding, this procedure can help increase gum tissue and protect your teeth. It’s a reliable method that has been used for decades to address gum health issues and improve oral aesthetics.
What Is a Free Gingival Graft?
A free gingival graft involves taking a small piece of tissue, usually from the roof of your mouth, and attaching it to the area where your gums need reinforcement. Unlike a connective tissue graft, this procedure uses the outer layer of tissue, which makes it ideal for increasing the width of your gums.
Your dentist carefully removes the tissue from the donor site and places it in the affected area. Over time, the graft integrates with your existing gums, creating a stronger and healthier gumline. This technique is particularly effective for patients with inadequate gum tissue or those needing additional keratinized tissue around their teeth.
Did you know? Free gingival grafts are considered the gold standard for gingival augmentation due to their predictability and long-term success.
Benefits of Free Gingival Grafts
You might wonder why this procedure is so highly regarded. Here are some of the key benefits:
Increases the width of keratinized gum tissue, improving gum health.
Protects exposed tooth roots from decay and sensitivity.
Enhances the appearance of your smile by creating a more even gumline.
Offers predictable outcomes with minimal graft shrinkage.
Allows for multiple teeth to be treated in a single procedure.
Clinical studies highlight the effectiveness of free gingival grafts. For example:
Success rates range from 76% to 95.5%, depending on patient cooperation with oral care.
This method is highly predictable for creating adequate keratinized tissue and halting advanced gingival recession.
While alternative grafting materials like acellular dermal matrix allografts may reduce surgical time, they lack the long-term reliability of free gingival grafts.
When Is a Free Gingival Graft Recommended?
Your dentist might recommend a free gingival graft if you have thin gums, exposed roots, or advanced gingival recession. This procedure is especially useful for patients who need to increase the width of their gum tissue to prevent further damage.
Here’s a quick look at when this procedure is most suitable:
Factor | Description |
|---|---|
Correcting gum recession | Repairs damage caused by gum recession and protects exposed roots. |
Improving appearance | Enhances your smile by addressing uneven or inadequate gum tissue. |
Enhancing oral health | Prevents decay of exposed roots and supports surrounding bone structures. |
If you’re comparing a free gingival graft vs connective tissue graft, the choice often depends on your specific needs. Free gingival grafts are ideal for increasing gum tissue, while connective tissue grafts excel in root coverage and cosmetic outcomes.
Tip: Discuss your goals with your dentist to determine the best option for your gum health.
Free gingival grafts are a tried-and-true method for improving gum health and appearance. With proper care, they can provide long-lasting results and help you maintain a healthy smile.
Healing and Recovery After a Free Gingival Graft
Recovering from a free gingival graft doesn’t have to feel intimidating. With the right care and a little patience, you’ll be back to your normal routine in no time. This procedure involves taking tissue from the roof of your mouth and attaching it to areas with thin or receding gums. While the surgery itself is straightforward, understanding the healing process can help you feel more confident about your treatment.
How Long Does Recovery Take?
Most patients heal from a free gingival graft within one to two weeks. However, recovery times can vary depending on factors like your overall health and how closely you follow post-operative instructions. During this period, the grafted tissue integrates with your gums, creating a stronger and healthier gumline.
Quick Tip: Stick to soft foods like scrambled eggs, smoothies, or mashed vegetables during the first few days. This reduces irritation and helps the graft site heal faster.
What to Expect During Recovery
You might notice some discomfort or swelling around the graft and donor sites. This is completely normal and usually subsides within a few days. Your dentist may recommend over-the-counter pain relievers or prescribe medication to keep you comfortable.
Here’s what you can expect:
Mild swelling and tenderness at the surgical sites.
A temporary change in the color or texture of your gums as they heal.
Restrictions on brushing or flossing near the graft site for the first week.
Your dentist will likely provide a special mouth rinse to keep the area clean and prevent infection. Follow their instructions carefully to ensure a smooth recovery.
Common Complications
While free gingival grafts are highly successful, complications can occasionally occur. Knowing what to watch for can help you address issues early. Some of the most common complications include:
Bleeding
Gum graft failure
Swelling
Infection
If you notice severe swelling, loosening sutures, or signs of infection, contact your dentist immediately. Early intervention can prevent further problems and ensure the best possible outcome.
Tips for a Faster Recovery
You play a big role in how quickly and smoothly you heal. Here are some tips to speed up the process:
Rest as much as possible during the first few days.
Avoid smoking or drinking alcohol, as these can delay healing.
Stick to a soft diet and avoid crunchy or spicy foods.
Follow all post-operative care instructions from your dentist.
By taking these steps, you can reduce discomfort and help your gums heal faster. A free gingival graft not only strengthens your gums but also protects your teeth from further damage. With proper care, the results can last a lifetime.
Did You Know? Compared to other grafting techniques, free gingival grafts are particularly effective for increasing gum tissue and preventing further gum recession.
Connective Tissue Graft vs Free Gingival Graft: Key Differences
Choosing between a connective tissue graft and a free gingival graft can feel tricky. Both procedures aim to improve gum health, but they differ in technique, healing, and effectiveness. Understanding these differences can help you make an informed decision with your dentist.
Procedure and Technique
The main difference lies in how each procedure is performed. A connective tissue graft involves harvesting tissue from underneath the roof of your mouth. This subepithelial technique focuses on connective tissue only, leaving the outer layer of the palate intact. Your dentist creates a small pouch in the affected area to secure the graft, ensuring it integrates seamlessly with your gums.
On the other hand, a free gingival graft uses both the epithelium and connective tissue. The tissue is taken directly from the roof of your mouth and placed over the recipient site. This method is ideal for increasing the width of gum tissue, especially in areas with inadequate keratinized tissue.
Here’s a quick comparison of the two techniques:
Feature | Connective Tissue Graft (CTG) | Free Gingival Graft (FGG) |
|---|---|---|
Tissue Source | Tissue taken from underneath the palate | Tissue taken from the roof of the mouth (palate) |
Composition | Only connective tissue | Both epithelium and connective tissue |
Procedure Steps | Incision made, pouch created for donor tissue, secured with sutures | Incision made, donor tissue placed over recipient site, secured with sutures |
Ideal Use | For thicker gum tissue or to increase volume | For thin gum tissue or to increase width |
While both methods are effective, the choice depends on your specific gum condition and goals.
Healing Time and Comfort
Healing time and comfort levels also vary between the two procedures. A connective tissue graft typically causes less discomfort because the outer layer of the palate remains intact. Most patients experience tenderness for 7-10 days, with full healing taking several weeks.
In contrast, a free gingival graft may involve more postoperative discomfort. Since the tissue is removed directly from the roof of your mouth, the donor site can feel sore for 2-4 days. However, the overall healing process is similar, with noticeable improvement within the first few weeks.
Graft Type | Average Healing Time |
|---|---|
Connective Tissue Graft | 7-10 days tenderness |
Free Gingival Graft | 2-4 days discomfort |
If comfort is a priority, you might lean toward a connective tissue graft.
Effectiveness for Treating Gum Recession
When it comes to the treatment of gingival recession, both procedures deliver excellent results. However, a connective tissue graft is often the preferred choice for severe cases. Studies show that techniques like the modified tunnel technique and coronal advanced flap (CAF) achieve up to 86% root coverage within the first year. This makes it highly effective for advanced gingival recession.
A free gingival graft, while effective, is better suited for increasing gum tissue width rather than achieving maximum root coverage. It’s a reliable option for patients with thin gums or those needing additional keratinized tissue.
Ultimately, the choice between a connective tissue graft vs free gingival graft depends on your specific needs. Discuss your goals with your dentist to determine the best option for your gum health.
Suitability for Different Gum Conditions
Not all gum grafting procedures are created equal. The type of graft you need depends on your specific gum condition. Your dentist will evaluate factors like gum thickness, the extent of recession, and your overall oral health to recommend the best option.
Here’s a quick breakdown of which conditions are better suited for each type of graft:
Connective Tissue Grafts (CTG):
Best for patients with exposed tooth roots caused by gum disease.
Ideal for treating advanced gum recession where root coverage is a priority.
Suitable for improving gum thickness and protecting teeth from further damage.
Free Gingival Grafts (FGG):
Perfect for patients with thinning gums that need reinforcement.
Recommended for increasing the width of keratinized gum tissue.
Effective for preventing further gum recession in areas with inadequate tissue.
If you’re comparing a free gingival graft vs connective tissue graft, think about your goals. Do you want to repair exposed roots or simply strengthen your gumline? CTGs excel at root coverage, while FGGs shine when it comes to augmenting thin gums.
Pro Tip: Always discuss your gum health goals with your dentist. They’ll help you choose the procedure that matches your needs and promises the best results.
Aesthetic Outcomes
When it comes to aesthetics, both grafting techniques can improve your smile, but they achieve this in different ways. Connective tissue grafts often provide superior cosmetic results, especially for patients dealing with exposed roots. Free gingival grafts, on the other hand, focus more on functional improvements like increasing gum tissue width.
Let’s compare the aesthetic outcomes of these two procedures:
Parameter | CTG (Mean ± SD) | FGG (Mean ± SD) | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|
Recession Depth (RD) Baseline | 4.68 ± 0.76 | 5.31 ± 1.35 | - |
Recession Depth (RD) Follow-up | 0.18 ± 0.34 | 0.43 ± 0.49 | - |
Keratinized Tissue Width (KTW) | 2.84 ± 1.12 | 5.25 ± 0.84 | P < 0.0001 |
Recession Aesthetic Score (RES) | Higher in CTG | Lower in FGG | P = 0.067 |
As you can see, CTGs tend to deliver better results for reducing recession depth and improving the overall appearance of your gums. The subepithelial technique used in CTGs ensures a natural color match between the graft and your existing gum tissue. This makes it a popular choice for patients seeking cosmetic restoration.
FGGs, while less focused on aesthetics, still offer significant benefits. They’re excellent for creating a strong, healthy gumline that supports your teeth and prevents further damage. If you’re more concerned about functionality than appearance, FGGs might be the way to go.
Did You Know? Studies show that CTGs achieve higher aesthetic scores compared to FGGs, making them the preferred option for patients prioritizing cosmetic outcomes.
When deciding between a free gingival graft vs connective tissue graft, consider what matters most to you—functionality, aesthetics, or both. Your dentist can guide you toward the procedure that aligns with your goals and ensures a healthy, beautiful smile.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Gum Grafting Procedure
Choosing the right gum grafting procedure can feel overwhelming, but understanding the key factors can make the decision easier. Your dentist will evaluate your gum health, the severity of your gum recession, and your long-term goals to recommend the best option. Let’s break it down step by step.
Severity of Gum Recession
The extent of your gum recession plays a major role in determining the most suitable grafting technique. If your gums have receded significantly, exposing the roots of multiple teeth, a connective tissue graft might be the better choice. This procedure provides excellent root coverage and is highly effective for treating advanced gingival recession. On the other hand, if your gums are naturally thin and you need to increase their width, a free gingival graft could be more appropriate.
Here’s a quick comparison of grafting techniques based on the severity of gum recession:
Grafting Technique | Description | Suitable For |
|---|---|---|
Connective Tissue Graft | A flap is created in the roof of the mouth, and connective tissue is transplanted to the receding area. | Treating multiple teeth |
Free Gingival Graft | Tissue is taken from the surface of the palate and grafted onto the affected gums. | Patients with naturally thin gums |
Pedicle Graft | Tissue is taken from an area close to the recession and pulled over the exposed root. | Patients with adequate nearby gum tissue |
Alternative Grafts | Donor tissue from human or animal sources may be used for severe cases. | Severe cases requiring complex grafting |
If you’re comparing free gingival graft vs connective tissue graft, think about how much root coverage you need. Connective tissue grafts excel in this area, while free gingival grafts are better for augmenting thin gums.
Thickness and Health of Existing Gum Tissue
The current state of your gum tissue is another critical factor. If your gums are thin or inadequate, a free gingival graft can help increase their width and provide additional keratinized tissue. This is especially important for protecting your teeth and preventing further gum recession.
For patients with thicker gums but exposed roots, a connective tissue graft is often the preferred option. This technique not only repairs the damage but also strengthens the surrounding tissue, offering long-term protection for your teeth. Dentists often recommend this method because of its predictability and ability to match the color and texture of your existing gums.
Tip: If you’re unsure about the health of your gums, ask your dentist to evaluate them during your next visit. They’ll help you understand which procedure aligns with your needs.
Long-Term Goals for Gum Health
Your long-term goals should guide your decision. Are you looking to improve the appearance of your smile, or is your primary concern protecting your teeth from further damage? Both procedures offer unique benefits, so it’s essential to consider what matters most to you.
Here are some long-term benefits of gum grafting to keep in mind:
Preserves the underlying bone, preventing tooth loss.
Protects exposed roots from decay and damage.
Encourages healthy gum tissue growth, reducing the risk of periodontal disease.
Enhances the aesthetic appearance of your gums and teeth.
Prevents further gum recession, avoiding more serious dental issues.
Provides long-lasting results when combined with good oral hygiene.
Studies show that connective tissue grafts tend to deliver better results for reducing recession depth, while free gingival grafts excel at increasing keratinized tissue width. For example:
Mean Recession Depth (RD): 0.18 ± 0.34 mm for connective tissue grafts vs. 0.43 ± 0.49 mm for free gingival grafts.
Keratinized Tissue Width (KTW): 2.84 ± 1.12 mm for connective tissue grafts vs. 5.25 ± 0.84 mm for free gingival grafts.
If you’re comparing free gingival graft vs connective tissue graft indications, think about whether you prioritize cosmetic outcomes or functional improvements. Your dentist can help you weigh these factors and choose the procedure that promises the best results for your gum health.
Recommendations from Your Periodontist
When it comes to choosing between a connective tissue graft and a free gingival graft, your periodontist plays a major role in guiding you toward the best option. They don’t just perform the procedure—they evaluate your gum health, discuss your goals, and recommend the treatment that promises the best results for your unique situation.
Why Trust Your Periodontist?
Periodontists specialize in diagnosing and treating gum-related issues. They’ve undergone extensive training in procedures like connective tissue grafts (CTG) and free gingival grafts (FGG). Their expertise ensures that your treatment is tailored to your needs, whether you’re dealing with receding gums, exposed roots, or inadequate gum tissue.
Did You Know? Periodontists often use advanced techniques like subepithelial connective tissue grafts to minimize discomfort and improve healing outcomes.
Your periodontist will assess factors like the severity of your gum recession, the thickness of your existing gum tissue, and your long-term oral health goals. They’ll also consider the aesthetic outcomes you’re hoping to achieve. For example, if you want to repair exposed roots and improve your smile, they might recommend a CTG. If your goal is to increase the width of your gums, an FGG could be the better choice.
What to Expect During Your Consultation
During your consultation, your periodontist will:
Examine your gums and teeth to determine the extent of the issue.
Discuss the differences between a free gingival graft vs connective tissue graft.
Explain how each procedure works, including the surgical techniques involved.
Address any concerns you have about healing, discomfort, or long-term results.
They’ll also use clinical studies and evidence to support their recommendations. For instance, studies show that CTGs provide excellent root coverage, while FGGs are ideal for increasing keratinized tissue. Your periodontist will help you understand these findings and how they apply to your case.
Questions to Ask Your Periodontist
Don’t hesitate to ask questions during your consultation. Here are a few to consider:
Which grafting technique is best for my gum condition?
What are the potential risks or complications of this procedure?
How long will it take for my gums to heal?
Will the graft match the color and texture of my existing gums?
What can I do to ensure the best possible outcome?
Tip: Bring a list of questions to your appointment. This ensures you don’t forget anything important and helps you feel more confident about your treatment plan.
Personalized Care for Long-Lasting Results
Your periodontist’s goal is to provide personalized care that addresses your specific needs. They’ll consider factors like your oral health history, the condition of your gums, and your lifestyle habits. By tailoring the procedure to your situation, they can ensure long-lasting results that improve both the health and appearance of your gums.
Whether you’re comparing a free gingival graft vs connective tissue graft or exploring other options, trust your periodontist to guide you every step of the way. Their expertise and commitment to your oral health make them the best resource for achieving a strong, healthy smile.
Remember: The right grafting procedure isn’t just about fixing a problem—it’s about creating a foundation for better gum health in the future.
Connective tissue grafts and free gingival grafts both play vital roles in gum grafting, but they serve different purposes. Connective tissue grafts excel in root coverage and cosmetic restoration, making them ideal for repairing receding gums and exposed roots. Free gingival grafts, on the other hand, focus on increasing gum tissue width, providing a strong foundation for long-term gum health.
Your choice between these procedures depends on your gum health, the severity of your gum recession, and your goals. Discussing factors like treatment customization, cost, and healing expectations with your periodontist ensures the best outcome. Their expertise helps tailor the procedure to your needs, whether you prioritize root coverage or gum reinforcement.
Remember: Gum grafting isn’t just about fixing a problem—it’s about creating a healthier, more confident smile. Consult your periodontist to determine the best option for your gum health goals.
FAQ
You might still have questions about gum grafting procedures. Here are some of the most common ones to help you better understand your options.
What’s the difference between a connective tissue graft and a free gingival graft?
A connective tissue graft (CTG) focuses on root coverage and improving gum thickness. A free gingival graft (FGG) increases gum tissue width. CTGs are ideal for cosmetic restoration, while FGGs are better for reinforcing thin gums. Your dentist will recommend the best option based on your needs.
How painful is a gum grafting procedure?
Most patients report mild discomfort rather than severe pain. Dentists use local anesthesia during the procedure, and over-the-counter pain relievers help manage post-surgery soreness. Connective tissue grafts often cause less discomfort compared to free gingival grafts due to the subepithelial technique.
How long does it take to heal after a gum graft?
Healing typically takes 4-8 weeks, depending on the procedure and your overall health. Connective tissue grafts usually heal faster and with less discomfort. Free gingival grafts may involve more soreness at the donor site but still heal within a similar timeframe.
Can gum grafts fail?
While rare, graft failure can occur due to infection, improper healing, or patient non-compliance with post-operative care. Following your dentist’s instructions, such as avoiding smoking and maintaining oral hygiene, significantly reduces the risk of complications.
Are gum grafts permanent?
Yes, gum grafts provide long-lasting results when properly cared for. They strengthen your gums, protect exposed roots, and prevent further recession. Regular dental check-ups and good oral hygiene ensure the graft remains healthy and effective.
Which procedure is better for cosmetic results?
Connective tissue grafts typically offer superior cosmetic outcomes. The subepithelial technique ensures a natural color match with your existing gums, making it ideal for patients seeking aesthetic restoration. Free gingival grafts focus more on functionality than appearance.
Can I eat normally after a gum graft?
You’ll need to stick to soft foods like yogurt, mashed potatoes, and smoothies for the first week. Avoid crunchy, spicy, or hard foods to prevent irritation. Gradually reintroduce regular foods as your gums heal.
How do I know which grafting procedure is right for me?
Your dentist or periodontist will evaluate your gum health, recession severity, and goals. They’ll explain the differences between free gingival graft vs connective tissue graft and recommend the best option for your specific needs. Always discuss your concerns during the consultation.
Tip: Don’t hesitate to ask your dentist about the procedure, healing process, and expected outcomes. Clear communication ensures you feel confident in your treatment plan.
See Also
Natural Versus Conventional Treatments for Gum Disease in 2025
Natural Solutions for Swollen Gums with ProDentim
The Impact of Stress on Gum Disease and Oral Health
