Gum Problems During Pregnancy: Hidden Risks Explained
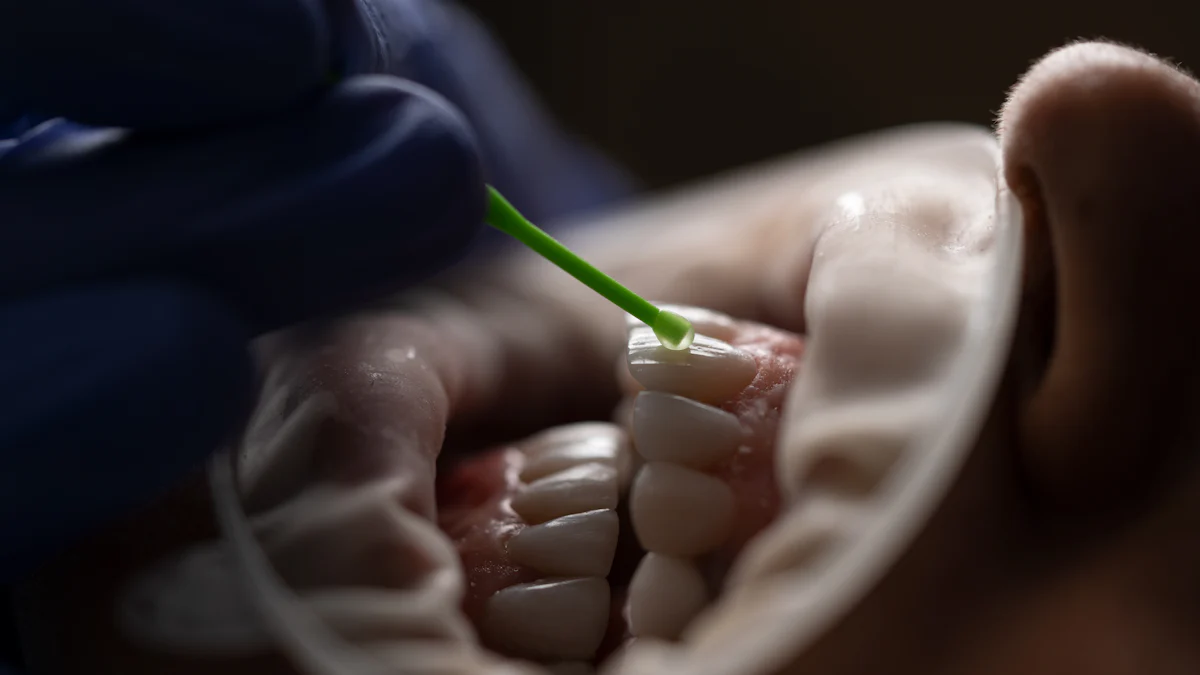
Gums problems during pregnancy, such as gingivitis and periodontal disease, are more common than you might think. Studies reveal that up to 89% of pregnant women in Ghana and 86.2% in Thailand experience gingivitis. These gums problems during pregnancy can lead to serious risks, including preterm birth and low birth weight. Bacteria from gum disease may enter your bloodstream, potentially affecting your baby. Gum inflammation caused by hormonal changes during pregnancy makes your gums more sensitive and prone to swelling or bleeding. Addressing these gums problems during pregnancy early can prevent complications for both you and your child.
Did you know? Pregnant women with periodontitis face six times the risk of premature birth compared to those without gum disease.
Common Gum Problems During Pregnancy
Pregnancy can bring significant changes to your body, including your oral health. Hormonal fluctuations during this time can make your gums more sensitive and prone to issues. Understanding these common gum problems can help you take proactive steps to protect your dental health and ensure a healthy pregnancy.
Pregnancy Gingivitis
Pregnancy gingivitis is one of the most common oral health issues expectant mothers face. It affects up to 40% of pregnancies and typically begins around the second month, peaking by the eighth month. You may notice symptoms like redness, swelling, tenderness, and bleeding gums, especially when brushing or flossing. These symptoms occur because hormonal changes, particularly increased levels of progesterone and estrogen, make your gums more susceptible to plaque buildup.
If left untreated, gingivitis can progress to more severe conditions like periodontal disease. Regular brushing, flossing, and dental checkups can help manage this condition.
Periodontal Disease
Periodontal disease, also known as periodontitis, is a more advanced stage of gum disease. It occurs when untreated gingivitis leads to the formation of pockets between your teeth and gums. These pockets can trap bacteria, causing inflammation and damage to the supporting tissues and bone. Symptoms include gum bleeding, gum recession, and even loose teeth.
This condition poses serious risks during pregnancy. Studies show that periodontal disease increases the likelihood of preterm birth and low birth weight. Maintaining good oral hygiene and seeking professional dental care can reduce these risks.
Other Oral Health Issues During Pregnancy
Pregnancy can also lead to other oral health problems beyond gingivitis and periodontal disease. You may experience:
Pregnancy tumors (epulis gravidarum): These non-cancerous growths on your gums can develop due to hormonal changes. They often appear red and swollen but usually resolve after delivery.
Enamel erosion: Morning sickness and stomach acid exposure can wear down your tooth enamel, increasing sensitivity.
Cavities: Dietary changes and increased snacking during pregnancy can raise your risk of tooth decay.
Loose teeth: Hormonal shifts can affect the ligaments and bones supporting your teeth, making them feel loose.
Addressing these issues early with proper dental care and hygiene can help you maintain a healthy mouth throughout your pregnancy.
How Untreated Gum Problems Affect Pregnancy Outcomes
Untreated gum problems during pregnancy can lead to serious health risks for both you and your baby. These issues, including gingivitis and periodontal disease, can cause complications that affect pregnancy outcomes. Understanding these risks can help you take steps to protect your health and your child’s well-being.
Preterm Birth and Low Birth Weight
Periodontal disease has been closely linked to preterm birth and low birth weight. When gum inflammation remains untreated, bacteria can enter your bloodstream and potentially reach the placenta. This bacterial infection can disrupt fetal development. Infections, including those caused by periodontal disease, account for 30% to 50% of premature and low birth weight cases.
Each year, approximately 15 million babies are born prematurely, often weighing less than 2500 grams. Babies born to mothers with untreated gum disease face a higher risk of respiratory issues, developmental delays, and growth challenges. By addressing gum problems early, you can reduce the likelihood of these adverse pregnancy outcomes.
Systemic Inflammation and Maternal Health Risks
Gum disease doesn’t just affect your mouth; it can trigger systemic inflammation throughout your body. This inflammation, while a natural response to infection, can harm your baby’s development. Bacteria from gum disease may spread through your bloodstream, potentially reaching the amniotic fluid or placenta. This can lead to complications such as premature birth or low birth weight.
Severe gum disease can also increase your stress levels due to pain and discomfort, indirectly impacting your baby’s health. Managing gum inflammation through proper dental care can help you avoid these risks and maintain a healthy pregnancy.
Long-Term Impacts on Maternal and Infant Health
The effects of untreated gum problems can extend beyond pregnancy. For you, periodontal disease may lead to chronic oral health issues, including tooth loss and gum recession. For your child, low birth weight and premature birth can result in long-term developmental challenges, such as learning disabilities or delayed motor skills.
Addressing gum problems while pregnant not only improves your oral health but also supports your baby’s growth and development. Regular dental checkups and good oral hygiene practices can help you prevent these long-term impacts.
Causes of Gum Problems During Pregnancy
Pregnancy brings many changes to your body, including shifts that can affect your oral health. These changes often make your gums more sensitive and prone to issues like gum inflammation and periodontal disease. Understanding the causes of these problems can help you take steps to protect your dental health during this critical time.
Hormonal Changes and Their Effects on Gums
Hormonal fluctuations during pregnancy play a significant role in gum problems. Increased levels of estrogen and progesterone make your gums more sensitive to plaque and bacteria. This sensitivity often leads to gum inflammation, redness, and tenderness. You may notice symptoms like bleeding gums, especially when brushing or flossing.
These hormonal changes can also cause pregnancy gingivitis, a mild form of gum disease that typically begins in the second trimester and peaks in the third. In some cases, you might develop pregnancy tumors, which are non-cancerous growths on the gums. These growths, referred to as epulis gravidarum, usually resolve after delivery. Maintaining good oral hygiene and visiting your dentist regularly can help manage these conditions.
Increased Blood Flow to Gums
During pregnancy, your body increases blood flow to support your growing baby. This increased blood volume can make your gums swell and become more prone to bleeding. Swollen gums may feel tender or sore, especially when brushing or eating. This condition, aggravated by plaque buildup, can lead to gum pain during pregnancy.
You can reduce the risk of gum problems by brushing and flossing daily to remove plaque. Regular dental checkups are also essential to monitor your gum health and address any issues early.
Altered Immune Response During Pregnancy
Your immune system undergoes changes during pregnancy to protect your baby. While these changes help prevent your body from rejecting the fetus, they also make you more susceptible to infections, including periodontal disease.
Evidence | Description |
|---|---|
PMNs Role | Polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMNs), which fight infections, function less effectively during pregnancy, increasing your risk of gum problems. |
Cytokine Release | Your body releases proinflammatory cytokines in response to bacteria, which can worsen gum inflammation. |
Immunosuppression | A natural suppression of your immune system during pregnancy increases your vulnerability to periodontal disease. |
These immune changes can lead to gum inflammation and exacerbate existing gum conditions. You can protect your oral health by maintaining a consistent hygiene routine and seeking professional dental care when needed.
Poor Oral Hygiene or Preexisting Conditions
Poor oral hygiene and preexisting conditions can significantly increase your risk of gum problems during pregnancy. When you neglect daily brushing and flossing, plaque builds up on your teeth. This sticky film of bacteria irritates your gums, causing redness, swelling, and bleeding. Pregnancy hormones, like progesterone and estrogen, amplify your gums' response to plaque, making them more prone to inflammation. Without proper care, this can lead to pregnancy gingivitis or even periodontitis.
Preexisting conditions, such as diabetes, can also worsen gum problems while pregnant. Diabetes affects your body’s ability to fight infections, including those in your gums. If you have diabetes, you may experience more severe gum inflammation and a higher risk of gum disease progression. Additionally, low levels of vitamin C, a common nutritional deficiency, can weaken your gum tissue, making it more susceptible to damage and infection.
Tip: Include vitamin C-rich foods like oranges, strawberries, and bell peppers in your diet to support healthy gums during pregnancy.
Here are some factors that can aggravate gum problems:
Hormonal changes during pregnancy increase your gums' sensitivity to plaque.
Poor oral hygiene allows plaque and tartar to accumulate, worsening gum inflammation.
Nutritional deficiencies, especially in vitamins and minerals, weaken your gum tissue.
If you already have gum disease when pregnant, it’s crucial to seek treatment early. Untreated gum problems can lead to severe gum pain during pregnancy and increase the risk of complications like preterm birth. Regular dental checkups, combined with daily brushing and flossing, can help you manage these risks. By addressing preexisting conditions and maintaining good oral hygiene, you can protect your gums and ensure a healthier pregnancy.
Note: Consult your dentist if you notice persistent gum pain, swelling, or bleeding. Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent long-term issues for you and your baby.
Preventative Measures and Treatment Options
Taking care of your gums during pregnancy is essential for maintaining your overall health and protecting your baby. By adopting simple preventative measures and seeking appropriate treatments, you can reduce the risk of gum inflammation and periodontal disease.
Daily Oral Hygiene Practices for Pregnant Women
Consistent oral hygiene is your first line of defense against gum problems while pregnant. Hormonal changes during pregnancy make your gums more sensitive and prone to inflammation, so maintaining a clean mouth is crucial.
Brush your teeth at least twice a day using fluoride toothpaste and a soft-bristled toothbrush. This helps remove plaque without irritating tender gums.
Floss daily to eliminate food particles and bacteria trapped between your teeth.
Consider using an antimicrobial mouthwash to reduce gum inflammation and prevent bacterial buildup.
Rinse your mouth with water or fluoride mouthwash after experiencing morning sickness to protect your enamel from stomach acid.
Stay hydrated and eat a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals to support gum health.
These habits can significantly decrease the occurrence of gum disease during pregnancy and keep your gums healthy.
Importance of Regular Dental Checkups During Pregnancy
Regular dental visits are vital for monitoring your gum health. Pregnant women should schedule checkups every six months or more frequently if recommended by their dentist. These visits allow your dentist to detect early signs of gum inflammation or periodontal disease and provide timely treatment.
Professional cleanings remove plaque and tartar that daily brushing and flossing might miss. Inform your dentist about your pregnancy and any medications you’re taking to ensure safe and effective care. Skipping dental checkups during pregnancy increases the risk of gum problems progressing to more severe conditions.
Safe and Effective Dental Treatments for Expectant Mothers
Dental treatments during pregnancy are safe and can prevent complications like preterm birth. The second trimester is the ideal time for procedures such as fillings, root canals, or tooth extractions. Local anesthetics like lidocaine are considered safe when used appropriately.
If you experience severe gum pain during pregnancy, consult your dentist immediately. Treating periodontal disease early can improve your health and reduce risks for your baby. Avoid sedatives like benzodiazepines, and ensure your dentist uses protective measures during any necessary X-rays.
By addressing gum problems promptly, you can protect your oral health and support a healthy pregnancy.
Dietary Considerations to Support Gum Health
Your diet plays a crucial role in maintaining healthy gums during pregnancy. The hormonal changes you experience can make your gums more sensitive and prone to inflammation. Eating the right foods can strengthen your gum tissue, reduce swelling, and lower the risk of gum disease.
A balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals supports your oral health and helps prevent common gum problems like gingivitis and periodontitis. Vitamin C is especially important because it promotes collagen production, which strengthens your gums and reduces bleeding. Include foods like oranges, strawberries, bell peppers, and broccoli in your meals to boost your vitamin C intake. Calcium is another essential nutrient. It helps maintain strong teeth and bones, reducing the risk of gum recession. Dairy products, leafy greens, and fortified plant-based milk are excellent sources of calcium.
Tip: Snack on crunchy fruits and vegetables like apples and carrots. They naturally clean your teeth and stimulate saliva production, which helps wash away bacteria.
Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fish like salmon and walnuts, have anti-inflammatory properties that can reduce gum swelling. Whole grains, rich in fiber, also support gum health by stabilizing blood sugar levels. High sugar levels can increase your risk of gum infections. Avoid sugary snacks and drinks, as they feed the bacteria that cause plaque buildup.
Staying hydrated is equally important. Drinking plenty of water helps flush out food particles and bacteria from your mouth. It also keeps your gums hydrated, reducing tenderness and soreness.
By making these dietary adjustments, you can protect your gums and ensure a healthier pregnancy. Pairing a nutrient-rich diet with daily brushing and flossing will give you the best chance of avoiding gum problems while pregnant.
Untreated gum problems during pregnancy can lead to serious risks for both you and your child. Conditions like gingivitis and periodontitis increase the chances of premature birth, low birth weight, and systemic inflammation. Hormonal changes during pregnancy make your gums more sensitive, causing swelling, redness, and bleeding. These changes also make you more prone to bacterial infection, which can affect pregnancy outcomes.
You can protect your health and your child’s well-being by prioritizing gum care. Early signs of gum disease, such as bleeding or swollen gums, should prompt immediate dental care. Regular brushing, flossing, and dental checkups are essential. A balanced diet rich in calcium and vitamin D also supports gum health. By taking these steps, you reduce risks and ensure healthier pregnancy outcomes for both you and your baby.
FAQ
What causes gum problems during pregnancy?
Hormonal changes, especially increased levels of progesterone and estrogen, make your gums more sensitive to plaque. This sensitivity can lead to inflammation, redness, and swelling. Increased blood flow to your gums and an altered immune response also contribute to gum problems during pregnancy.
Can gum disease during pregnancy harm my baby?
Yes, untreated gum disease can increase the risk of preterm birth and low birth weight. Bacteria from your gums may enter your bloodstream and reach the placenta, potentially affecting your baby’s development. Addressing gum problems early reduces these risks.
How can I prevent gum problems while pregnant?
Brush your teeth twice daily with fluoride toothpaste and floss daily. Visit your dentist regularly for checkups and cleanings. Eat a balanced diet rich in vitamin C and calcium to support gum health. Avoid sugary snacks and drinks to reduce plaque buildup.
Is it safe to visit the dentist during pregnancy?
Yes, dental visits are safe and essential during pregnancy. Inform your dentist about your pregnancy. The second trimester is the best time for treatments like cleanings or fillings. Avoid elective procedures in the first and third trimesters unless necessary.
What should I do if I experience gum pain during pregnancy?
If you notice gum pain, swelling, or bleeding, consult your dentist immediately. Early treatment can prevent the condition from worsening. Use a soft-bristled toothbrush and rinse with an antimicrobial mouthwash to reduce discomfort.
See Also
Simple Ways to Achieve Healthier Gums While Pregnant
Effective Methods for Managing Gum Issues in Pregnancy
Essential Advice for Maintaining Gum Health in Pregnancy
Understanding Hormonal Shifts and Their Impact on Gum Health
