Why Hormonal Changes Trigger Gums Problems During Pregnancy
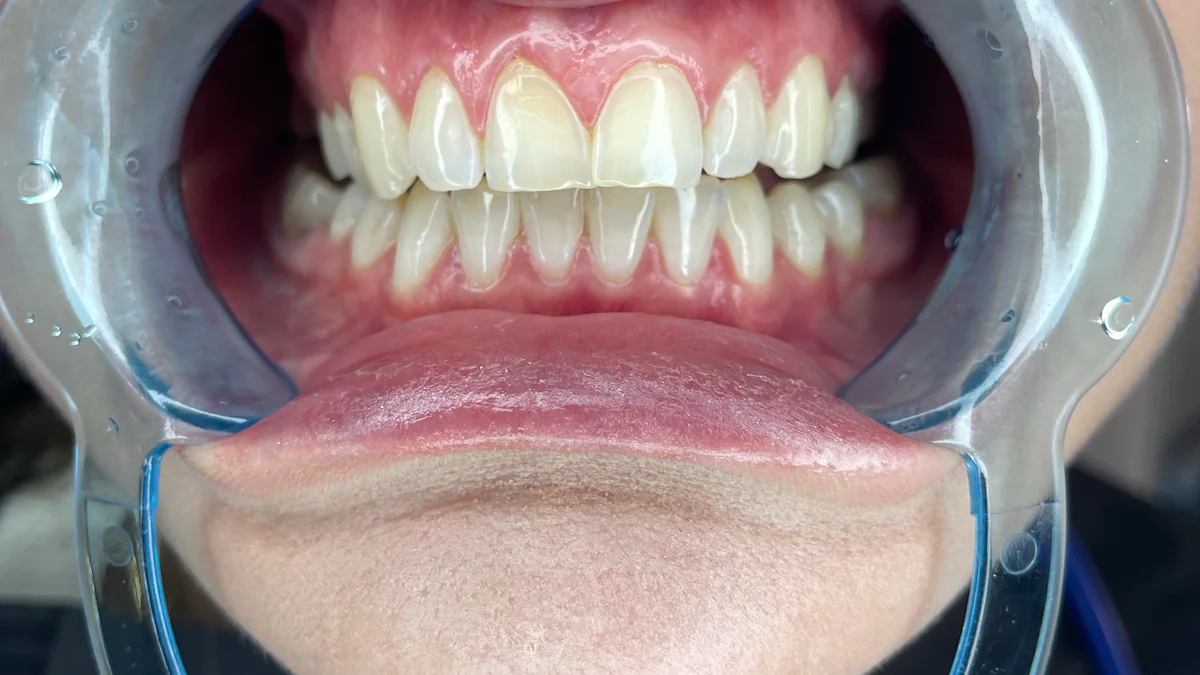
Pregnancy brings significant hormonal changes that can affect your oral health, leading to gums problems during pregnancy. These changes often make your gums more sensitive and prone to inflammation. Increased levels of estrogen and progesterone cause your blood vessels to dilate, leading to swelling and redness in the gums. They also weaken your immune response, making it harder for your body to fight bacteria in your mouth. As a result, you may experience pregnancy gingivitis, a condition where your gums become tender, swollen, and bleed easily, especially during brushing or flossing. Studies show that up to 75% of pregnant women develop gingivitis, with some regions reporting even higher rates. Ignoring these symptoms can lead to more severe gum problems during pregnancy, such as periodontal disease or even pregnancy tumors. Understanding these changes helps you take steps to protect your gum health and prevent complications.
What Hormonal Changes Occur During Pregnancy?
During pregnancy, your body undergoes significant hormonal changes that affect various systems, including your oral health. These changes prepare your body to support the growing baby but can also make your gums more sensitive and prone to problems. Understanding these hormonal shifts helps you take better care of your gums and teeth during this critical time.
Increased Progesterone and Estrogen Levels
Progesterone and estrogen levels rise dramatically during pregnancy. These hormones play essential roles in maintaining a healthy pregnancy, but they also impact your gum tissues. Progesterone increases vascular permeability, causing your gums to swell and become tender. Estrogen enhances blood flow to the gums, which can lead to redness and inflammation. These changes make your gums more susceptible to irritation from plaque and bacteria.
The hormonal fluctuations also alter the immune response in your mouth. Progesterone suppresses local immune defenses, allowing bacteria to grow more easily. This can lead to conditions like pregnancy gingivitis, where your gums become inflamed and bleed during brushing or flossing. Studies show that 60–70% of pregnant women experience this condition, especially during the second trimester.
Enhanced Blood Flow to Gums
Pregnancy increases blood volume in your body to support the baby’s development. This enhanced blood flow affects your gums, making them more sensitive and prone to swelling. The increased blood supply can cause your gums to appear redder than usual and feel sore or tender. You might notice that your gums bleed more easily when you brush or floss.
This heightened sensitivity is a common issue during pregnancy and is often aggravated by plaque buildup. If plaque isn’t removed through regular brushing and flossing, it can harden into tartar, further irritating your gums. Maintaining good oral hygiene is crucial to prevent these problems from worsening.
Changes in Immune System Function
Your immune system undergoes significant changes during pregnancy to protect the baby. These changes include a shift toward an anti-inflammatory state, which helps prevent your body from rejecting the fetus. However, this shift can also weaken your ability to fight infections, including those in your mouth.
The suppression of certain immune cells, like neutrophils, makes your gums more vulnerable to bacterial infections. This can lead to increased inflammation and a higher risk of gum disease during pregnancy. You may notice symptoms like gum pain, swelling, and bleeding, even if your oral hygiene routine hasn’t changed. These issues highlight the importance of regular dental checkups during pregnancy to monitor and manage your gum health.
Impact on Collagen Production and Tissue Repair
Hormonal changes during pregnancy don’t just affect your gums’ sensitivity. They also influence how your body produces and repairs collagen, a vital protein that supports gum tissues. Collagen plays a key role in maintaining the strength and elasticity of your gums, but pregnancy hormones can disrupt this process, making your gums more vulnerable to damage.
How Hormones Affect Collagen Levels
During pregnancy, increased levels of progesterone and estrogen can interfere with collagen production. Progesterone, in particular, slows down the body’s ability to produce new collagen fibers. This reduction weakens the structural integrity of your gum tissues, making them more prone to swelling, tenderness, and bleeding. Estrogen, while essential for blood flow, can also alter the balance of enzymes responsible for breaking down and rebuilding collagen. These hormonal fluctuations create an environment where your gums struggle to repair themselves effectively after daily wear and tear caused by brushing, flossing, or chewing.
Delayed Tissue Repair and Gum Health
When your body’s ability to repair gum tissues slows down, even mild gum problems can escalate. For example, if you experience pregnancy gingivitis, the inflammation caused by plaque buildup can persist longer than usual. Your gums may remain red, swollen, and tender because the damaged tissues take more time to heal. This delayed healing increases the risk of more severe conditions like periodontitis, a form of advanced gum disease that can lead to gum recession and tooth loss if untreated.
Tip: To support tissue repair during pregnancy, focus on maintaining a healthy diet rich in vitamin C and other nutrients that promote collagen production. Foods like oranges, strawberries, and bell peppers can help strengthen your gums.
Why Collagen Matters for Gum Problems While Pregnant
Collagen isn’t just important for healing. It also helps your gums stay firm and resistant to bacterial infections. When collagen levels decrease, your gums become more susceptible to bacteria that cause gum disease during pregnancy. This vulnerability can lead to symptoms like gum pain, bleeding, and swelling. In severe cases, the weakened gum tissues may even form small growths called pregnancy tumors, which are non-cancerous but can cause discomfort.
Supporting Healthy Collagen Production
You can take steps to protect your gums and support collagen production during pregnancy. Regular dental checkups allow your dentist to monitor your gum health and address any issues early. Brushing and flossing daily help remove plaque, reducing the strain on your gums. Staying hydrated also supports tissue health by improving blood flow to your gums. If you notice persistent symptoms like bleeding or soreness, consult your dentist for advice on safe treatments.
Note: Hormonal changes are a natural part of pregnancy, but they don’t have to lead to gum problems. With proper care, you can keep your gums healthy and reduce the risk of long-term issues.
By understanding how pregnancy hormones impact collagen production and tissue repair, you can take proactive steps to protect your oral health. Healthy gums not only benefit you but also contribute to a healthier pregnancy and baby.
How Do Hormonal Changes Affect Gum Health?
Hormonal changes during pregnancy can significantly impact your gum health. These changes make your gums more sensitive, alter how your body responds to plaque and bacteria, and increase the risk of inflammation and infection. Understanding these effects can help you take better care of your oral health during this critical time.
Increased Gum Sensitivity
Pregnancy hormones, particularly estrogen and progesterone, play a major role in increasing gum sensitivity. These hormones cause the tiny blood vessels in your gums to dilate, leading to increased blood flow. This heightened blood flow makes your gums more tender and prone to swelling. You may notice that your gums bleed more easily when brushing or flossing.
Several mechanisms link hormonal changes to this increased sensitivity:
Hormonal fluctuations during pregnancy lead to the dilation of blood vessels in the gums.
This dilation increases blood flow, making your gums more sensitive to bacteria and toxins from plaque.
Immunological changes impair immune cell function, leaving your gums more susceptible to inflammation.
You might experience gum pain during pregnancy, even with mild irritation. This sensitivity often worsens if plaque builds up, so maintaining a consistent oral hygiene routine is essential.
Altered Response to Plaque and Bacteria
Your body’s response to plaque and bacteria changes during pregnancy due to hormonal fluctuations. Higher levels of progesterone and estrogen increase blood supply to your gums, making them more prone to swelling and bleeding. This altered response can lead to pregnancy gingivitis, a condition where your gums become red, swollen, and tender.
Here’s how hormonal changes affect your gums:
Surges in progesterone make your gums more susceptible to bacterial plaque.
Estrogen enhances vascular permeability, causing fluid to accumulate in your gum tissues.
These changes stimulate an inflammatory response, resulting in symptoms like redness, swelling, and bleeding.
If left untreated, this inflammation can progress to more severe conditions like periodontal disease. Regular brushing and flossing can help reduce plaque buildup and minimize these risks.
Higher Risk of Inflammation and Infection
Hormonal changes during pregnancy increase your risk of gum inflammation and infection. Pregnancy induces a degree of immunosuppression, which weakens your body’s ability to fight bacteria in your mouth. This makes your gums more vulnerable to conditions like gingivitis and periodontitis.
Studies show that pregnant women often have a higher gingival index (GI) and periodontal pocket depth (PPD) compared to nonpregnant women, even with similar plaque levels. This suggests that hormonal changes, rather than poor oral hygiene, are the primary cause of increased gum inflammation during pregnancy.
The changes in your immune system also affect the subgingival microbiota, the bacteria that live below your gumline. These bacteria can trigger an exaggerated inflammatory response, leading to symptoms like gum pain, swelling, and bleeding. If you notice persistent symptoms, consult your dentist for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
Tip: To reduce your risk of gum inflammation, brush and floss daily, use pregnancy-safe oral care products, and schedule regular dental checkups.
By understanding how hormonal changes affect your gum health, you can take proactive steps to prevent complications and maintain a healthy smile throughout your pregnancy.
Role of Hormones in Pregnancy Gingivitis
Hormonal changes during pregnancy play a significant role in the development of pregnancy gingivitis. This condition, which affects a large percentage of pregnant women, occurs due to the combined effects of increased hormone levels, vascular changes, and altered immune responses. Understanding how these factors contribute to gingivitis can help you take steps to protect your gum health.
How Hormones Trigger Gingivitis
During pregnancy, your body produces higher levels of estrogen and progesterone. These hormones are essential for supporting your baby’s growth, but they also affect your gums. Progesterone increases blood vessel permeability, leading to swelling and tenderness in the gum tissues. Estrogen enhances blood flow to the gums, making them appear red and inflamed. These changes make your gums more sensitive and prone to irritation from plaque and bacteria.
Hormones also influence your immune system. Progesterone suppresses certain immune responses, allowing bacteria to thrive in your mouth. This creates an environment where plaque can accumulate more easily, increasing the risk of gum inflammation. Research shows that these hormonal shifts directly impact cytokine production in your gums. Cytokines are proteins that regulate inflammation, and their imbalance can worsen gingivitis symptoms like redness, swelling, and bleeding.
The Link Between Hormones and Bacterial Growth
Elevated hormone levels during pregnancy can alter the balance of bacteria in your mouth. Studies have found that progesterone enhances the production of prostaglandin E2, a compound that promotes inflammation. This makes your gums more susceptible to bacterial infections. Additionally, estrogen and progesterone increase the production of interleukin-6 and interleukin-8, which are inflammatory markers linked to periodontal disease progression. These changes explain why pregnancy gingivitis often worsens during the second trimester, when hormone levels peak.
Why Pregnancy Gingivitis Is Common
Pregnancy gingivitis affects 60-70% of pregnant women, making it one of the most common oral health issues during this stage. The condition is primarily caused by the hormonal fluctuations that occur during pregnancy. These fluctuations increase your gums’ sensitivity to plaque, even if your oral hygiene routine remains consistent. If left untreated, pregnancy gingivitis can progress to more severe conditions like periodontitis, which may lead to gum recession or tooth loss.
Note: Hormonal changes don’t mean you have to suffer from gingivitis. Regular brushing, flossing, and dental checkups can help you manage symptoms and maintain healthy gums.
Managing Hormonal Effects on Your Gums
You can reduce the impact of hormonal changes on your gums by maintaining a consistent oral hygiene routine. Brush your teeth twice a day with a soft-bristled toothbrush and use pregnancy-safe toothpaste. Floss daily to remove plaque from areas your toothbrush can’t reach. Schedule regular dental checkups to monitor your gum health and address any issues early. A balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals can also support your gum tissues and reduce inflammation.
Pregnancy gingivitis is a common but manageable condition. By understanding the role of hormones in its development, you can take proactive steps to protect your oral health and ensure a healthier pregnancy.
Common Gum Problems During Pregnancy
Pregnancy can bring several changes to your oral health, especially your gums. Hormonal fluctuations during this time increase your risk of developing gum-related issues. These problems often result from heightened sensitivity, inflammation, and changes in how your body responds to bacteria. Understanding these common gum problems can help you take steps to protect your oral health.
Pregnancy Gingivitis
Pregnancy gingivitis is one of the most common gum problems during pregnancy. It occurs due to increased levels of progesterone and estrogen, which make your gums more sensitive and prone to inflammation. This condition often peaks during the second trimester and can worsen if left untreated.
Symptoms of pregnancy gingivitis include:
Red, swollen gums
Tenderness in the gum area
Increased bleeding when brushing or flossing
These symptoms result from hormonal changes that aggravate existing gingivitis or create a favorable environment for plaque buildup. Studies show that pregnancy gingivitis affects 60-70% of pregnant women, with prevalence rates as high as 89% in some regions like Ghana.
To manage this condition, brush your teeth twice daily with a soft-bristled toothbrush and floss regularly. Schedule dental checkups to monitor your gum health. A balanced diet rich in vitamins can also support your gums and reduce inflammation.
Tip: If you notice persistent symptoms like bleeding or soreness, consult your dentist for advice on safe treatments.
Swollen and Bleeding Gums
Swollen and bleeding gums are another common issue during pregnancy. Hormonal changes increase blood flow to your gums, making them more sensitive and prone to swelling. This heightened sensitivity can cause your gums to bleed easily, especially during brushing or flossing.
Plaque buildup often worsens these symptoms. If not removed, plaque hardens into tartar, further irritating your gums and increasing the risk of infection. You may also experience gum pain or tenderness, which can make daily oral hygiene challenging.
To reduce swelling and bleeding, maintain a consistent oral hygiene routine. Use pregnancy-safe toothpaste and mouthwash to clean your teeth and gums gently. Staying hydrated and eating foods rich in vitamin C can also support healthy gum tissues.
Note: Swollen and bleeding gums are common but manageable. Early intervention can prevent more severe conditions like periodontal disease.
Periodontal Disease Risks
Periodontal disease, or gum disease, poses a significant risk during pregnancy. Approximately 40% of pregnant women experience some form of periodontal disease, with higher rates among smokers and those with poor oral hygiene. This condition occurs when untreated gingivitis progresses, leading to gum recession, tooth loss, and even systemic health issues.
Hormonal changes weaken your immune response, making it harder for your body to fight bacteria in your mouth. This allows plaque to accumulate below the gumline, causing inflammation and infection. Symptoms of periodontal disease include persistent bad breath, gum recession, and loose teeth.
Research links periodontal disease during pregnancy to serious complications, including preterm birth and low birth weight. The bacteria from infected gums can enter your bloodstream, potentially affecting your baby’s health.
To lower your risk, brush and floss daily, and visit your dentist regularly for professional cleanings. Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent periodontal disease from progressing.
Alert: If you experience severe gum pain, loose teeth, or other concerning symptoms, seek immediate dental care.
Pregnancy Tumors (Pyogenic Granulomas)
Pregnancy tumors, also called pyogenic granulomas, are non-cancerous growths that can develop on your gums during pregnancy. These growths, which affect up to 5% of pregnant women, often appear as small, red, or purple lumps on the gumline. While they may look alarming, they are typically harmless and tend to shrink or disappear after childbirth.
What Causes Pregnancy Tumors?
Hormonal changes during pregnancy play a significant role in the development of these tumors. Here’s how hormones contribute:
Hormonal Imbalances: Increased levels of estrogen and progesterone during pregnancy can lead to vascular malformations in your gums.
VEGF Production: Estrogen enhances the production of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), which promotes the formation of new blood vessels in the gum tissues. This process may contribute to the growth of pregnancy tumors.
Immune Response: Progesterone acts as an immunosuppressant, altering your body’s inflammatory response and making your gums more reactive to plaque and bacteria.
These factors create an environment where your gums become more susceptible to developing these growths, especially if plaque buildup aggravates the condition.
Symptoms and Management
Pregnancy tumors often cause discomfort, especially when brushing or flossing. You might notice bleeding, tenderness, or swelling around the affected area. Although these growths are usually painless, their location can make eating or speaking uncomfortable.
To manage pregnancy tumors:
Maintain a consistent oral hygiene routine to reduce plaque buildup.
Use a soft-bristled toothbrush to avoid irritating the growth.
Visit your dentist for regular checkups. They can monitor the tumor and recommend safe treatments if necessary.
In most cases, pregnancy tumors resolve on their own after delivery. However, if the growth causes severe discomfort or interferes with daily activities, your dentist may suggest removing it.
Tip: Don’t ignore unusual growths on your gums. Early diagnosis ensures proper care and prevents complications.
Long-Term Effects on Gum Health
Pregnancy-related gum problems can have lasting effects on your oral health if left untreated. Hormonal changes during pregnancy increase your risk of developing conditions like gingivitis and periodontitis, which can lead to serious consequences over time.
Progression to Periodontitis
Untreated gingivitis can progress to periodontitis, a severe form of gum disease that damages the tissues and bones supporting your teeth. This condition can cause gum recession, tooth loss, and even systemic health issues. Studies show that approximately 40% of pregnant women experience some form of periodontal disease, highlighting the importance of early intervention.
Impact on Overall Health
Gum disease during pregnancy doesn’t just affect your mouth. Research links periodontal disease to serious health conditions, including cardiovascular disease and diabetes. The bacteria from infected gums can enter your bloodstream, potentially reaching the placenta. This may trigger premature labor or low birth weight in babies. In fact, about 18% of premature, low birth weight infants are born to mothers with periodontal disease.
Preventing Long-Term Issues
You can protect your oral health by addressing gum problems early. Brush and floss daily to remove plaque and prevent inflammation. Schedule regular dental checkups to monitor your gum health and receive professional cleanings. A balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals also supports healthy gums and reduces the risk of complications.
Alert: Severe gum pain during pregnancy or persistent symptoms like bleeding and swelling require immediate attention. Consult your dentist to prevent long-term damage.
By understanding the potential long-term effects of pregnancy-related gum problems, you can take proactive steps to maintain a healthy smile and support your overall well-being. Healthy gums benefit not only you but also your baby’s development.
How to Manage and Prevent Gum Problems
Managing gum problems during pregnancy is essential for maintaining your oral health and preventing complications. Hormonal changes increase your gums' sensitivity and make them more prone to inflammation. By adopting a proactive approach, you can protect your gums and ensure a healthier pregnancy.
Maintain a Consistent Oral Hygiene Routine
A consistent oral hygiene routine is your first line of defense against gum problems. Pregnancy hormones, like progesterone and estrogen, increase your gums' susceptibility to plaque and bacteria. Brushing and flossing daily help remove plaque and reduce the risk of gingivitis and periodontitis.
Brush your teeth twice a day using a soft-bristled toothbrush. This minimizes irritation to your tender gums while effectively cleaning your teeth. Use an anti-gingivitis toothpaste, such as Crest Gum Detoxify Deep Clean, to target bacteria that cause gum inflammation. Floss daily with a product like Oral-B Glide® PRO-HEALTH® Clinical Protection Floss to clean areas your toothbrush cannot reach.
Pay special attention to the gum line, where plaque tends to accumulate. If brushing or flossing causes discomfort, try rinsing with an alcohol-free, antibacterial mouthwash like Crest® PRO-HEALTH® Multi-Protection Mouthwash. This helps reduce bacteria and soothes your gums.
Tip: Inform your dentist and hygienist about your pregnancy. They can provide tailored advice and adjust your dental care routine to suit your needs.
Use Pregnancy-Safe Oral Care Products
Choosing the right oral care products during pregnancy is crucial for protecting your gums and teeth. Some ingredients in regular products may irritate your gums or pose risks to your baby. Opt for pregnancy-safe options that are gentle yet effective.
Look for fluoride toothpaste to strengthen your enamel and prevent cavities. Baking soda-based products are safe and help whiten your teeth without harming your gums. Alcohol-free mouthwash prevents dry mouth and reduces gum irritation. Antibacterial mouthwash can also help control plaque and prevent gum disease during pregnancy.
Natural ingredients like aloe vera, coconut oil, and essential oils offer additional benefits. These ingredients soothe inflammation and support gum health. Always check product labels and consult your dentist if you are unsure about a specific product.
Note: Avoid products with harsh whitening agents or alcohol, as they can aggravate gum sensitivity.
Schedule Regular Dental Checkups
Regular dental checkups are vital for monitoring your gum health during pregnancy. Hormonal changes can cause gum problems to develop or worsen quickly. Professional cleanings remove plaque and tartar that brushing and flossing cannot eliminate.
Inform your dentist about your pregnancy at the earliest opportunity. This allows them to tailor your care and recommend safe treatments. Schedule at least one dental visit per trimester to stay ahead of potential issues. If you experience symptoms like swollen or bleeding gums, don’t wait for your next appointment. Seek prompt care to prevent complications.
Dental visits during pregnancy are safe and beneficial. Your dentist can diagnose and treat conditions like pregnancy gingivitis or periodontal disease before they escalate. They may also provide tips on maintaining oral hygiene and suggest dietary changes to support your gum health.
Alert: Severe gum pain during pregnancy or persistent symptoms like redness and swelling require immediate attention. Early intervention ensures better outcomes for you and your baby.
By maintaining a consistent oral hygiene routine, using pregnancy-safe products, and scheduling regular dental checkups, you can effectively manage and prevent gum problems. These steps not only protect your gums but also contribute to a healthier pregnancy and baby.
Eat a Balanced Diet Rich in Vitamins
Your diet plays a crucial role in maintaining gum health during pregnancy. The right nutrients strengthen your gums, reduce inflammation, and support tissue repair. A balanced diet not only benefits your oral health but also contributes to your baby’s development.
Vitamin D is essential for healthy teeth and gums. It reduces inflammation and strengthens the periodontium, the tissues that support your teeth. Adequate levels of vitamin D lower the risk of pregnancy gingivitis, a common condition caused by hormonal changes. Vitamin K2 works alongside vitamin D to ensure proper calcium absorption, which keeps your teeth and bones strong. Foods like salmon, fortified cereals, and leafy greens are excellent sources of these vitamins.
Incorporating a variety of nutrient-rich foods into your meals can further protect your gums. Here are some key nutrients to include:
Vitamin C: Found in strawberries, oranges, and kiwi, it boosts your immune system and promotes healthy gums.
Beta-carotene: Present in sweet potatoes and carrots, it converts to vitamin A, which supports oral tissue health.
Omega-3 fatty acids: Found in nuts and fish, they help manage inflammation in your gums.
Calcium: Essential for strong teeth and bones, it is abundant in dairy products and leafy greens.
Tip: Aim for a colorful plate at every meal. The more variety you include, the better your chances of getting all the nutrients your gums need.
Avoid Sugary Foods and Drinks
Sugary foods and drinks can worsen gum problems during pregnancy. They feed harmful bacteria in your mouth, leading to plaque buildup and increasing your risk of gingivitis and cavities. Pregnancy hormones already make your gums more sensitive and prone to inflammation, so limiting sugar intake becomes even more important.
When you consume sugary snacks or beverages, the bacteria in your mouth produce acids that attack your tooth enamel. This process can lead to tooth decay and aggravate gum sensitivity. Sticky sweets, like candy or caramel, are particularly harmful because they cling to your teeth and gums, prolonging exposure to sugar.
Instead of sugary treats, choose healthier alternatives:
Replace soda with water or unsweetened herbal tea.
Snack on fresh fruits like apples or pears, which are naturally sweet and help clean your teeth.
Opt for whole-grain crackers or nuts instead of cookies or chips.
Alert: Always check food labels for hidden sugars. Ingredients like high-fructose corn syrup or sucrose can sneak into processed foods and drinks.
By reducing your sugar intake, you can protect your gums from further irritation and maintain better oral health throughout your pregnancy.
Stay Hydrated to Support Oral Health
Staying hydrated is vital for your gum health during pregnancy. Water helps flush out food particles and bacteria from your mouth, reducing plaque buildup. It also keeps your gums and oral tissues moist, preventing discomfort caused by dryness.
Pregnancy often increases your risk of dry mouth, a condition that can lead to gum pain and bad breath. Hormonal changes may reduce saliva production, which is essential for neutralizing acids and washing away bacteria. Drinking plenty of water helps combat this issue and supports your overall oral hygiene.
To stay hydrated:
Drink at least 8-10 glasses of water daily.
Carry a reusable water bottle to sip throughout the day.
Include water-rich foods like cucumbers, watermelon, and celery in your diet.
Note: Avoid sugary or caffeinated drinks, as they can dehydrate you and worsen gum problems.
Proper hydration not only supports your gum health but also benefits your baby’s development. By making water your go-to beverage, you can keep your gums healthy and reduce the risk of pregnancy-related oral issues.
When to See a Dentist
Knowing when to visit a dentist during pregnancy is essential for protecting your oral health and preventing complications. Hormonal changes can make your gums more sensitive and prone to inflammation, increasing the risk of gum disease. Recognizing the signs of serious gum problems and seeking timely care ensures a healthier pregnancy for you and your baby.
Signs That Require Immediate Attention
Certain symptoms indicate that you should see a dentist without delay. Ignoring these signs can lead to severe gum problems or even affect your overall health. Watch for the following:
Swollen, bleeding gums that don’t improve with brushing or flossing
Severe or persistent bleeding after brushing
Excessive swelling or pain in your gums
Gums that appear red, shiny, or tender to the touch
Loose teeth or new spaces forming between teeth
Pus along the gumline or a fever, which may signal an infection
Mouth sores or lumps on your gums, including pregnancy tumors
Receding gums or toothache that worsens over time
Alert: If you experience any of these symptoms, schedule a dental appointment immediately. Early intervention can prevent more serious conditions like periodontitis or tooth loss.
Importance of Professional Dental Care During Pregnancy
Professional dental care plays a vital role in maintaining your oral health during pregnancy. Hormonal fluctuations increase your susceptibility to gum disease, making regular checkups more important than ever. Dentists can identify and treat issues early, ensuring they don’t escalate into more severe problems.
Here’s why professional care matters:
Regular dental visits help detect gum disease, cavities, or other oral health issues early.
Maintaining good oral hygiene reduces the risk of pregnancy complications like preterm labor.
Professional cleanings remove plaque and tartar that brushing and flossing can’t eliminate.
Dentists provide personalized advice on managing gum sensitivity and inflammation.
Neglecting your oral health during pregnancy can lead to complications. Research links untreated gum disease to premature birth and low birth weight in babies. By prioritizing dental care, you protect both your health and your baby’s development.
Tip: Inform your dentist about your pregnancy. They can tailor treatments to ensure safety for you and your baby.
Safe Dental Treatments for Pregnant Women
Many dental treatments are safe during pregnancy, especially when performed under professional guidance. Dentists take precautions to minimize risks and ensure your comfort. Preventive, diagnostic, and emergency treatments can all be safely managed during this time.
Here are some safe options:
Routine cleanings and plaque control help prevent gum disease.
Scaling, polishing, and curettage address mild to moderate gum problems.
Emergency treatments like extractions or root canals can be performed when necessary.
Local anesthetics with epinephrine are safe for pain management.
Radiographs are used selectively and only when absolutely needed.
Note: Avoid elective dental procedures during the second half of the third trimester. Always consult your obstetrician before undergoing any treatment.
Open communication between your dentist and prenatal caregiver ensures the best care. Dentists may ask about your due date or any specific concerns related to your pregnancy. This collaboration helps create a safe treatment plan tailored to your needs.
By recognizing the signs of gum problems, prioritizing professional care, and understanding safe treatment options, you can maintain healthy gums throughout your pregnancy. Healthy gums contribute to a healthier pregnancy and a brighter smile.
The Long-Term Impact of Gum Health on Pregnancy
Your gum health during pregnancy doesn’t just affect you—it can also have lasting consequences for your baby. Hormonal changes increase your risk of gum problems, which can lead to complications like preterm birth and developmental challenges. Understanding these risks helps you take proactive steps to protect both your oral health and your baby’s well-being.
Connection Between Gum Health and Preterm Birth
Gum disease during pregnancy can increase the risk of preterm birth. This occurs because inflammation caused by gum problems triggers a systemic response in your body. When bacteria from your gums enter your bloodstream, they can reach the placenta or amniotic fluid, potentially affecting your baby’s development.
Gum disease can cause systemic inflammation, which may interfere with fetal growth.
Bacteria from infected gums can travel through your bloodstream, increasing the risk of complications.
Severe gum disease is linked to a higher likelihood of premature delivery and low birth weight.
Maternal stress caused by gum pain or discomfort can indirectly impact your baby’s health.
Studies show that women with untreated gum disease are more likely to deliver prematurely. Babies born early often face challenges like underdeveloped organs or low birth weight, which can affect their long-term health. By addressing gum problems early, you reduce these risks and support a healthier pregnancy.
Tip: Regular dental checkups during pregnancy can help identify and treat gum disease before it leads to complications.
Effects on Baby’s Health and Development
Your oral health plays a critical role in your baby’s development. Gum disease during pregnancy doesn’t just increase the risk of preterm birth—it can also have direct effects on your baby’s health.
Bacteria from gum infections can reach the placenta, potentially causing infections in the baby.
Severe gum disease is associated with low birth weight, which may lead to developmental delays.
Poor gum health can result in cavities, which may transfer harmful bacteria to your baby after birth.
Babies born to mothers with untreated gum problems face a higher risk of early childhood cavities. This occurs because bacteria from your mouth can transfer to your baby through saliva. Maintaining healthy gums during pregnancy helps protect your baby from these risks and ensures better overall health.
Alert: If you experience severe gum pain during pregnancy, consult your dentist immediately. Early treatment can prevent complications for both you and your baby.
Importance of Postpartum Oral Care
Caring for your gums doesn’t end after delivery. Postpartum oral care is essential for preventing long-term complications and protecting your baby’s health. Hormonal changes during pregnancy can weaken your gums, making them more susceptible to infections even after childbirth.
Untreated gum problems can lead to systemic health issues, such as diabetes or cardiovascular disease.
Bacteria from your gums can transfer to your baby, increasing their risk of tooth decay.
Children of mothers with untreated cavities are three times more likely to develop cavities themselves.
Postpartum dental visits allow your dentist to assess your gum health and address any lingering issues. Regular brushing, flossing, and professional cleanings help restore your gums to a healthy state. A balanced diet rich in vitamins also supports tissue repair and reduces inflammation.
Note: Healthy gums benefit both you and your baby. By prioritizing postpartum oral care, you set the foundation for a lifetime of good oral health for your child.
Taking care of your gums during and after pregnancy ensures better outcomes for you and your baby. Healthy gums reduce the risk of complications, support your baby’s development, and promote long-term oral health for your entire family.
Hormonal changes during pregnancy can significantly impact your gum health, leading to common issues like gingivitis, swollen gums, and gum pain during pregnancy. These changes make your gums more sensitive and prone to inflammation, increasing the risk of gum problems while pregnant. However, you can take proactive steps to protect your oral health and prevent complications.
To maintain healthy gums, follow these key practices:
Brush your teeth twice daily and floss daily to remove plaque.
Visit your dentist regularly for checkups and cleanings.
Eat a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and dairy while limiting sugars and starches.
Practice relaxation techniques like yoga or deep breathing to reduce stress.
By understanding the connection between hormones and gum problems, you can manage these issues effectively. A consistent oral hygiene routine, combined with professional dental care and a healthy diet, ensures better gum health for you and your baby.
FAQ
What causes gum problems during pregnancy?
Hormonal changes, especially increased progesterone and estrogen, make your gums more sensitive and prone to inflammation. These hormones increase blood flow to your gums and weaken your immune response, allowing bacteria to grow. This combination often leads to conditions like pregnancy gingivitis or swollen gums.
Why do my gums bleed more when I brush during pregnancy?
Pregnancy hormones increase blood flow to your gums, making them more tender and prone to bleeding. Plaque buildup worsens this sensitivity. Brushing or flossing can irritate your gums, causing them to bleed more easily. Maintaining good oral hygiene helps reduce this issue.
Is gum disease during pregnancy harmful to my baby?
Yes, untreated gum disease can increase the risk of preterm birth and low birth weight. Bacteria from infected gums may enter your bloodstream and affect your baby’s development. Regular dental checkups and proper oral care reduce these risks and support a healthy pregnancy.
Can I treat gum problems while pregnant?
Yes, you can safely treat gum problems during pregnancy. Dentists recommend professional cleanings, scaling, and using pregnancy-safe oral care products. Avoid elective procedures in the third trimester. Always inform your dentist about your pregnancy to ensure safe treatments.
How can I prevent gum problems during pregnancy?
Brush twice daily with a soft-bristled toothbrush, floss daily, and use pregnancy-safe mouthwash. Eat a balanced diet rich in vitamins like C and D. Avoid sugary foods and drinks. Schedule regular dental checkups to monitor your gum health and address issues early.
Are swollen gums normal during pregnancy?
Yes, swollen gums are common due to increased blood flow and hormonal changes. This condition, called pregnancy gingivitis, affects many women. Symptoms include redness, tenderness, and swelling. Proper oral hygiene and regular dental visits help manage this issue.
Should I see a dentist if I have gum pain during pregnancy?
Yes, consult your dentist if you experience persistent gum pain, swelling, or bleeding. These symptoms may indicate gum disease or other oral health issues. Early diagnosis and treatment prevent complications and ensure better outcomes for you and your baby.
Will gum problems go away after pregnancy?
Most pregnancy-related gum problems improve after childbirth as hormone levels stabilize. However, untreated conditions like periodontitis can cause long-term damage. Continue practicing good oral hygiene and schedule postpartum dental visits to maintain healthy gums.
Tip: Address gum problems early to avoid lasting effects on your oral health.
See Also
Effective Strategies to Avoid Gum Bleeding While Pregnant
The Impact of Stress on Gum Health and Disease
Natural Relief for Swollen Gums with ProDentim
