How Can You Tell If Gum Disease Is Affecting You
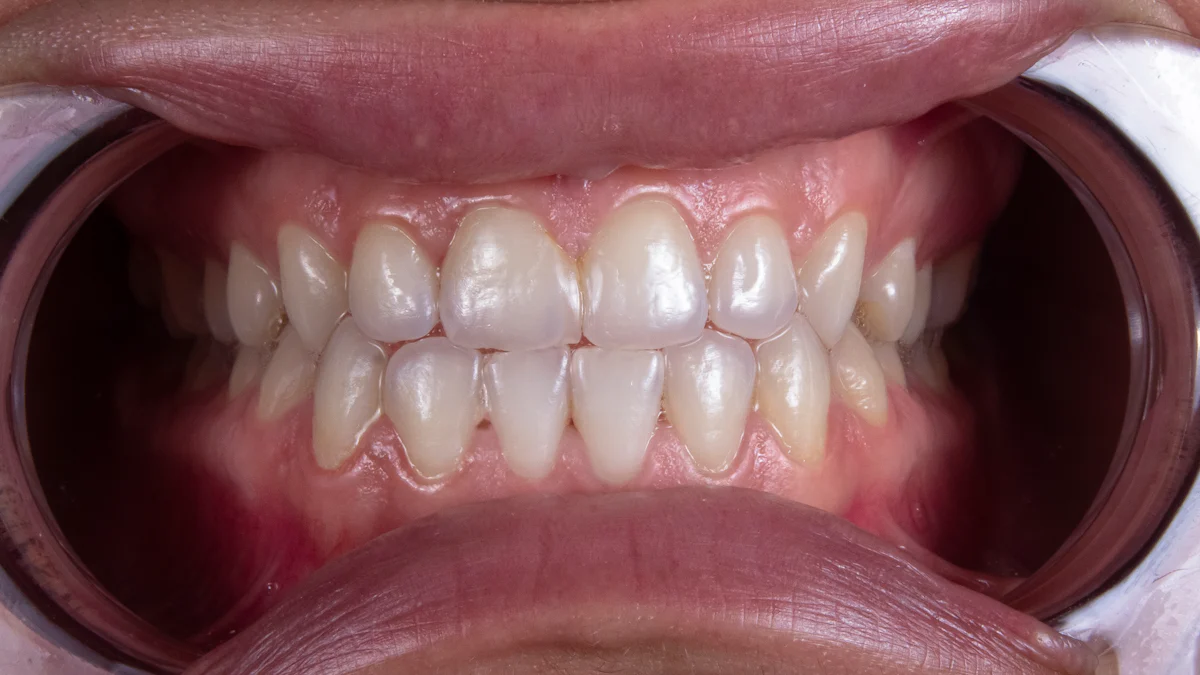
Do your gums bleed when you brush or floss? This could be an early sign of gum disease. Swollen gums, persistent bad breath, or receding gums may also indicate a problem. If you're wondering how can you tell if you have gum disease, nearly 47% of adults in the United States experience symptoms like bleeding gums or bad breath, making gum disease a common condition. Early detection is critical. Ignoring these signs can lead to severe issues like tooth loss or even systemic health problems. If you notice any of these symptoms, consult a dentist immediately. Taking action now can protect your oral health and prevent costly treatments later.
Common Signs of Gum Disease
Gum disease often starts with subtle symptoms that are easy to overlook. However, recognizing these early warning signs can help you take action before the condition worsens. Below are some of the most common signs of gum disease and what they may indicate about your oral health.
Bleeding Gums
Do your gums bleed when you brush or floss? This is one of the earliest and most noticeable signs of gum disease. Healthy gums should not bleed easily, even during daily brushing or flossing. Bleeding often occurs because plaque builds up along the gumline, causing inflammation. This inflammation, known as gingivitis, makes your gums more sensitive and prone to bleeding.
Many people mistakenly believe that bleeding gums are normal, especially after flossing. However, consistent bleeding is a red flag that your gums may be inflamed or infected. If left untreated, this condition can progress to more severe stages of gum disease, such as periodontitis. Pay attention to this symptom and consult your dentist if it persists.
Swollen or Tender Gums
Swelling or tenderness in your gums is another common indication of gum disease. When bacteria and plaque irritate the gum tissue, it can cause your gums to become puffy, red, or sore to the touch. You might notice that your gums feel tender when you eat, brush, or floss.
Healthy gums should appear firm and pink. If your gums look bright red, purplish, or feel painful, it’s time to take action. Swollen gums are often a sign that your body’s immune system is responding to an infection in the gum tissue. Without proper treatment, this inflammation can lead to gum recession, loose teeth, or even bone loss.
Persistent Bad Breath
Bad breath that doesn’t go away, even after brushing or using mouthwash, could be a sign of gum disease. This occurs because bacteria trapped in plaque and tartar release foul-smelling toxins. These toxins not only cause bad breath but also contribute to gum inflammation and infection.
Persistent bad breath, also known as halitosis, is more than just a nuisance. It can indicate that harmful bacteria are thriving in your mouth, potentially leading to more serious dental problems. If you notice a constant unpleasant taste or odor, it’s essential to address the underlying cause with your dentist.
Note: Gum disease doesn’t only affect older adults. It can occur at any age, even in children and teenagers. Don’t ignore these symptoms, regardless of your age.
By recognizing these signs of gum disease early, you can take steps to protect your oral health and prevent more severe complications. Regular dental checkups and good oral hygiene habits are key to keeping your gums healthy.
Gum Recession
Have you noticed your teeth appearing longer than usual? This could be a sign of gum recession. Gum recession occurs when the gum tissue surrounding your teeth pulls back, exposing more of the tooth or even its root. This condition often develops as a result of gum disease. It can also make your teeth more sensitive and prone to decay.
Receding gums are not just a cosmetic issue. They create pockets where bacteria can accumulate, leading to further damage. You might experience symptoms like sensitivity to hot or cold foods, visible roots, or even loose teeth. If left untreated, gum recession can progress to more severe stages of periodontal disease.
Treatment options for gum recession vary depending on its severity. Common treatments include:
Scaling and root planing to remove plaque and tartar buildup.
Antibiotics to fight infection.
Chlorhexidine rinses to prevent bacterial growth.
Gum grafting to restore lost tissue and protect exposed roots.
Regeneration procedures to encourage natural tissue growth.
If you notice signs of gum recession, consult your dentist promptly. Early intervention can prevent further damage and improve your oral health.
Changes in Bite or Tooth Alignment
Have you felt your teeth shifting or your bite changing? These changes can indicate advanced gum disease. As gum disease progresses, it can weaken the structures that support your teeth, including the bone. This can cause your teeth to loosen or move, altering how they fit together when you bite or chew.
You might notice difficulty chewing, discomfort when biting, or even gaps forming between your teeth. These changes often occur because the inflammation and infection caused by gum disease lead to bone loss. Without proper treatment, this can result in tooth loss.
Regular dental checkups can help detect these changes early. Dentists use tools like X-rays to assess bone health and identify any shifting teeth. If you experience changes in your bite, seek professional advice immediately. Treatments like deep cleaning, antibiotics, or even surgical interventions can help stabilize your teeth and restore your bite.
Tooth Sensitivity to Hot and Cold
Do you wince when sipping hot coffee or eating ice cream? Tooth sensitivity to hot and cold is a common symptom of gum disease. This sensitivity often occurs because receding gums expose the tooth roots, which lack the protective enamel found on the rest of the tooth.
Exposed roots are more vulnerable to temperature changes, causing discomfort or pain. You might also notice other symptoms like inflamed gums, persistent bad breath, or a foul taste in your mouth. These signs often indicate gum disease in its early or advanced stages.
To manage sensitivity, your dentist may recommend treatments like fluoride varnishes, desensitizing toothpaste, or gum grafting to cover exposed roots. Addressing the underlying gum disease is crucial to prevent further damage and reduce sensitivity.
If you experience tooth sensitivity, don’t ignore it. Consult your dentist to determine the cause and explore treatment options. Early action can save your teeth and improve your quality of life.
Why Do These Signs of Gum Disease Occur?
Understanding why gum disease develops can help you take better care of your oral health. The symptoms you notice, such as bleeding gums or bad breath, often stem from specific processes happening in your mouth. Let’s explore the key factors behind these signs.
The Role of Plaque and Tartar
Plaque is a sticky film of bacteria that forms on your teeth every day. When you eat or drink, the bacteria in plaque feed on sugars and release acids. These acids irritate your gums and cause inflammation. If you don’t remove plaque through daily brushing and flossing, it hardens into tartar. Tartar is a rough, yellowish deposit that builds up along your gumline and can only be removed by a dentist.
Tartar creates a rough surface where more bacteria can thrive, making it harder to keep your gums healthy. Over time, this buildup leads to redness, swelling, and bleeding. These are early signs of gum disease, such as gingivitis. If left untreated, the condition can progress to periodontitis, a more severe stage of gum disease.
To prevent plaque and tartar from causing damage, focus on consistent oral hygiene. Brush twice a day, floss daily, and visit your dentist regularly for professional cleanings.
How Inflammation Affects Gum Tissue
Inflammation is your body’s natural response to infection. When bacteria from plaque invade your gums, your immune system activates to fight back. This process causes your gums to become red, swollen, and tender.
Research shows that an unhealthy oral microbiome triggers specialized immune cells called T helper 17 (Th17) cells. These cells play a significant role in gum disease by causing inflammation and tissue destruction. Studies have found that people with periodontitis have higher levels of Th17 cells in their gum tissue. The severity of the disease often correlates with the presence of these cells.
While inflammation is meant to protect your body, chronic inflammation in your gums can do more harm than good. It weakens the gum tissue, making it easier for bacteria to penetrate deeper into your mouth. This can lead to gum recession, persistent bad breath, and even tooth loss.
The Connection Between Gum Disease and Bone Loss
Gum disease doesn’t just affect your gums—it can also harm the bones that support your teeth. As the infection spreads, it damages the structures that hold your teeth in place. This includes the jawbone, which can begin to deteriorate over time.
When bacteria and toxins from plaque and tartar reach below the gumline, they create pockets of infection. These pockets allow bacteria to multiply and release toxins that break down bone tissue. As the bone weakens, your teeth may start to loosen or shift. You might notice changes in your bite or gaps forming between your teeth.
Bone loss is a serious consequence of advanced gum disease, such as periodontitis. Without treatment, it can lead to tooth loss and permanent damage to your jaw. Regular dental checkups and early intervention are essential to prevent this outcome. Treatments like scaling and root planing or periodontal surgery can help stop the progression of bone loss and restore your oral health.
By understanding the causes behind gum disease, you can take proactive steps to protect your teeth and gums. Pay attention to the signs, maintain good oral hygiene, and seek professional care when needed.
Stages of Gum Disease
Gum disease progresses through distinct stages, each with unique symptoms and levels of severity. Understanding these stages can help you recognize the condition early and seek timely treatment. The two primary stages of gum disease are gingivitis and periodontitis.
Gingivitis (Early Stage)
Gingivitis is the initial stage of gum disease. At this stage, the condition primarily affects your gums, causing mild inflammation. You might notice symptoms like redness, swelling, and bleeding when brushing or flossing. These signs often appear painless, making it easy to overlook the problem.
The primary cause of gingivitis is plaque buildup along the gumline. Plaque contains bacteria that irritate your gums, leading to inflammation. If you don’t remove plaque daily through brushing and flossing, it hardens into tartar, which worsens the condition.
Fortunately, gingivitis is reversible with proper oral hygiene and professional dental cleanings. If you notice early signs like bleeding gums or persistent bad breath, take action immediately. Ignoring these symptoms can allow the disease to progress to a more severe stage.
Condition | Symptoms | Severity |
|---|---|---|
Gingivitis | Red, swollen gums; bleeding when brushing or flossing; often painless. | Mild inflammation of gums. |
Periodontitis (Advanced Stage)
If gingivitis goes untreated, it can advance to periodontitis. This stage involves severe inflammation that affects not only your gums but also the bone and tissues supporting your teeth. You may experience symptoms like receding gums, loose teeth, and persistent bad breath. In some cases, you might notice pus or discharge coming from your gums.
Periodontitis occurs when bacteria and toxins from plaque and tartar invade deeper into your gums. This creates pockets of infection that damage the surrounding bone and tissue. Over time, the condition can lead to gum recession, bone loss, and even tooth loss.
Long-term effects of untreated periodontitis include:
Gum recession
Bone damage
Tooth loss
Periodontitis is the leading cause of tooth loss in adults worldwide. It can significantly impact your quality of life, affecting your ability to chew and speak comfortably. If you suspect you have periodontitis, consult your dentist immediately. Treatments like scaling and root planing, antibiotics, or periodontal surgery can help manage the condition and prevent further damage.
Condition | Symptoms | Severity |
|---|---|---|
Periodontitis | Bleeding and sore gums; sensitive teeth; loose teeth; receding gums. | Severe inflammation, potential tooth loss. |
Recognizing the stages of gum disease early can save your teeth and gums from irreversible damage. Pay attention to the warning signs and maintain regular dental checkups to protect your oral health.
Risk Factors for Gum Disease
Certain factors can increase your risk of developing gum disease. Understanding these risks can help you take proactive steps to protect your oral health. Let’s explore some of the most common risk factors and how they contribute to gum problems.
Poor Oral Hygiene
Neglecting your oral hygiene can significantly increase your risk of gum disease. When you don’t brush or floss regularly, plaque builds up on your teeth. This sticky film contains bacteria that irritate your gums and cause inflammation. Over time, plaque hardens into tartar, which can only be removed by a dentist.
Evidence | Description |
|---|---|
Prevalence | Almost half of all adults in the United States have some form of gum disease. |
Cause | Buildup of dental plaque is the No. 1 cause of periodontal disease. |
Progression | Poor oral hygiene leads to plaque accumulation, which can infect the gums and progress to more severe forms of gum disease. |
Failing to maintain good oral hygiene can lead to gingivitis, the earliest stage of gum disease. Symptoms like bleeding gums, redness, and swelling often appear at this stage. If left untreated, gingivitis can progress to periodontitis, a more advanced condition that damages the bone and tissues supporting your teeth.
To reduce your risk, brush your teeth twice a day, floss daily, and visit your dentist regularly for professional cleanings. These simple habits can prevent plaque buildup and keep your gums healthy.
Smoking and Tobacco Use
Smoking is one of the most significant risk factors for gum disease. It disrupts the balance of bacteria in your mouth, allowing harmful bacteria to thrive. Toxic substances in cigarettes weaken your immune system, making it harder for your gums to fight infections. This increases your risk of developing periodontal disease and other oral health problems.
Smokers often experience more severe symptoms of gum disease, such as receding gums, loose teeth, and persistent bad breath. Smoking also reduces blood flow to your gums, which slows down healing and makes treatments less effective.
If you smoke, quitting can dramatically improve your oral health. Talk to your dentist or healthcare provider about resources to help you stop smoking. Your gums and overall health will thank you.
Genetics and Family History
Your genetic makeup can influence your susceptibility to gum disease. Studies show that certain genetic factors can increase your risk of developing periodontal disease. These genes may affect how your body responds to inflammation, making your gums more prone to damage from bacterial infections.
Evidence | Description |
|---|---|
Genetic susceptibility | The genetic component plays a key role in the onset of periodontal disease (PD). |
Inflammation modulation | Genetics can modulate the inflammation of mucous membranes and the loss of alveolar bone. |
Association with PD | Previous studies suggest a strong association between PD occurrence and individual genetic profiles. |
If gum disease runs in your family, you may need to take extra precautions to protect your oral health. Regular dental checkups, good oral hygiene, and a healthy lifestyle can help minimize your risk. Discuss your family history with your dentist to create a personalized prevention plan.
By understanding these risk factors, you can take steps to reduce your chances of developing gum disease. Pay attention to your oral hygiene, avoid smoking, and stay informed about your genetic risks. These actions can help you maintain healthy gums and a confident smile.
Underlying Health Conditions (e.g., diabetes)
Certain health conditions can make you more vulnerable to gum disease. Diabetes is one of the most significant examples. If you have diabetes, you may face a higher risk of gum problems due to the way this condition affects your body. Understanding this connection can help you take better care of your oral health.
Diabetes increases your chances of developing gum disease by altering your body’s natural defenses. High blood sugar levels can lead to increased glucose in your saliva. This extra glucose creates an ideal environment for harmful bacteria to grow. These bacteria can irritate your gums, causing inflammation and infection. Over time, this can lead to symptoms like redness, swelling, and bleeding. If untreated, gum disease can progress to more severe stages, such as periodontitis, which may result in tooth loss.
You might notice that your gums feel tender or bleed more easily if you have diabetes. This happens because diabetes slows down your body’s ability to heal. When your gums become inflamed, they take longer to recover. This delay allows the condition to worsen, leading to gum recession or even bone loss. You may also experience persistent bad breath or a foul taste in your mouth, which are common signs of gum infection.
Managing your blood sugar levels plays a crucial role in protecting your gums. When your blood sugar is under control, your body can fight off infections more effectively. Regular brushing and flossing can also help remove plaque and prevent bacteria from building up along your gumline. If you notice any signs of gum disease, such as swollen or bleeding gums, consult your dentist immediately. Early treatment can prevent complications and improve your overall health.
Other health conditions, like heart disease or autoimmune disorders, can also impact your gum health. However, diabetes remains one of the most common contributors. By staying vigilant and maintaining good oral hygiene, you can reduce your risk and keep your gums healthy.
Tip: If you have diabetes, schedule regular dental checkups. Your dentist can monitor your gum health and provide treatments to prevent or manage gum disease.
When to Seek Help for Gum Disease
Recognizing when to seek professional help for gum disease can save your teeth and gums from irreversible damage. While early symptoms like bleeding or swollen gums may seem minor, they can quickly escalate if left untreated. Knowing when to act ensures you receive timely care and prevent further complications.
Recognizing When Symptoms Worsen
Certain warning signs indicate that gum disease is progressing and requires immediate attention. These symptoms often suggest that the condition has moved beyond the early stage of gingivitis and may now involve more severe damage to your gums and supporting structures. Watch for the following:
Tooth sensitivity when consuming hot or cold foods or drinks.
Persistent bad breath that doesn’t improve with brushing or flossing.
Red, swollen, or puffy gums that feel tender or painful when touched.
Receding gums, where the gum tissue pulls back, exposing the roots of your teeth.
Loose or shifting teeth, which may affect how your bite fits together.
If you notice any of these symptoms, don’t wait. These signs often indicate advanced gum disease, such as periodontitis, which can lead to tooth loss if untreated. Acting quickly can prevent further damage and improve your oral health.
Importance of Regular Dental Checkups
Regular dental checkups play a vital role in preventing and managing gum disease. Even if your gums feel healthy, routine visits allow your dentist to detect early signs of trouble before they become severe. Professional cleanings remove plaque and tartar buildup that daily brushing and flossing can’t reach.
Dentists also monitor your gum health over time, checking for changes in color, texture, or sensitivity. They can identify issues like gum recession, inflammation, or pockets of infection that may not be visible to you. By catching these problems early, your dentist can recommend treatments to stop the progression of gum disease and protect your teeth.
Skipping dental checkups increases your risk of developing advanced gum disease. Make it a priority to schedule visits at least twice a year, or more often if your dentist recommends it.
What to Expect During a Gum Disease Evaluation
If you suspect gum disease, your dentist will perform a thorough evaluation to assess the condition of your gums and teeth. This process involves several diagnostic tools and procedures to determine the severity of the disease and the best course of treatment.
During the evaluation, your dentist may:
Use a periodontal probe to measure the depth of pockets around your teeth. Deeper pockets often indicate more advanced gum disease.
Check for bleeding on probing (BOP), which helps gauge the level of inflammation and infection.
Examine your teeth and gums for plaque and tartar buildup using sharp explorers or manual probes.
Take X-rays to assess bone levels and detect any loss of supporting structures.
These diagnostic steps provide a clear picture of your oral health and help your dentist create a personalized treatment plan. Early detection and intervention are key to managing gum disease effectively. If you’re experiencing symptoms like persistent bad breath, receding gums, or tooth sensitivity, schedule an evaluation as soon as possible.
Tip: Don’t let barriers like anxiety or financial concerns stop you from seeking care. Many dental offices offer payment plans or sedation options to make treatment more accessible and comfortable.
Preventing Gum Disease
Preventing gum disease starts with consistent care and attention to your oral health. By adopting effective daily habits, scheduling professional cleanings, and making lifestyle changes, you can protect your gums and teeth from damage. These steps not only help you avoid gum disease but also improve your overall well-being.
Daily Oral Hygiene Practices
Your daily oral hygiene routine plays a critical role in preventing gum disease. Simple yet effective habits can keep your gums healthy and free from plaque buildup. Follow these steps to maintain optimal oral health:
Brush Twice a Day: Brush your teeth for at least two minutes each time using a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste. This removes plaque and prevents it from hardening into tartar.
Floss Daily: Flossing removes food particles and plaque from areas your toothbrush cannot reach, such as between teeth and along the gumline.
Use an Antimicrobial Mouthwash: Rinse with an antimicrobial mouthwash to reduce bacteria and freshen your breath.
Replace Toothbrushes Regularly: Change your toothbrush every three to four months or sooner if the bristles become frayed.
Maintain Regular Dental Visits: Schedule dental checkups and cleanings at least twice a year to remove tartar and monitor your gum health.
These practices prevent plaque buildup, which is the leading cause of gum disease. Consistency is key. Make these habits part of your daily routine to protect your gums and teeth.
Professional Cleanings and Maintenance
Professional dental cleanings are essential for preventing gum disease. Even with excellent oral hygiene, plaque can harden into tartar, which only a dentist can remove. Regular cleanings ensure your gums stay healthy and free from infection.
Dentists recommend scheduling professional cleanings every six months. This bi-annual routine helps prevent gum disease and maintains overall oral health.
If you have risk factors like a history of gum disease, your dentist may suggest more frequent cleanings.
During a cleaning, your dentist or hygienist will remove tartar, polish your teeth, and check for early signs of gum disease.
Regular cleanings also allow your dentist to catch problems early. Early detection means less invasive treatments and better outcomes for your gums and teeth.
Lifestyle Changes to Support Gum Health
Your lifestyle choices significantly impact your gum health. Small changes can make a big difference in preventing gum disease and keeping your mouth healthy.
Quit Smoking: Smoking weakens your immune system and makes it harder for your gums to fight infections. Quitting smoking improves blood flow to your gums and enhances healing.
Eat a Balanced Diet: Foods rich in vitamins C and D, calcium, and antioxidants support gum health. Avoid sugary snacks and drinks that feed harmful bacteria.
Manage Stress: Chronic stress can weaken your immune system, making you more susceptible to gum disease. Practice relaxation techniques like meditation or yoga.
Stay Hydrated: Drinking water helps wash away food particles and bacteria, keeping your mouth clean and reducing the risk of gum disease.
Public health campaigns, like Japan’s 8020 Campaign, emphasize the importance of maintaining healthy teeth and gums throughout life. These efforts have shown that education and awareness can lead to better oral health outcomes. By adopting healthy habits, you can protect your gums and enjoy a confident smile.
Tip: Combine daily oral hygiene with regular dental visits and a healthy lifestyle for the best results. Prevention is always easier and less costly than treatment.
You can prevent or treat gum disease if you catch it early. Pay close attention to symptoms like bleeding gums, persistent bad breath, or gum recession. These signs often indicate the early stages of gum problems, such as gingivitis. Ignoring them can lead to more severe conditions like periodontitis, which may result in tooth loss.
Regular dental visits are essential for maintaining healthy gums. Dentists can detect early warning signs and provide treatments to stop the disease from progressing. By understanding the risks and taking preventive steps, you empower yourself to protect your oral health. If you notice any symptoms, consult your dentist without delay.
Tip: Educating yourself about gum disease and its consequences can help you take control of your oral health. Prevention is always better than treatment.
FAQ
How can you tell if you have gum disease?
You might notice symptoms like bleeding gums, persistent bad breath, or swollen and tender gums. Other signs include gum recession, loose teeth, or changes in your bite. If these symptoms occur, consult your dentist for an evaluation.
How do you tell if you have gingivitis?
Gingivitis manifests as red, swollen, or bleeding gums, especially during brushing or flossing. It’s the earliest stage of gum disease and is often painless. Early treatment can reverse this condition and restore healthy gums.
How can you tell if you have receding gums?
Receding gums appear as teeth looking longer than usual. You may also feel sensitivity to hot or cold foods. This condition creates pockets where bacteria can build up, leading to further gum damage.
How can you tell if you have a gum infection?
A gum infection often causes redness, swelling, and pain. You might notice pus, a foul taste, or persistent bad breath. These symptoms require immediate attention to prevent further complications.
How can you tell if you have periodontitis?
Periodontitis includes symptoms like gum recession, loose teeth, and deep pockets around the teeth. You may also experience bone loss and chronic inflammation. This advanced stage of gum disease needs professional treatment.
How do you tell if you have bad gums?
Bad gums feel tender, bleed easily, and may appear red or purplish. They can also feel puffy or sore when touched. These signs indicate gum disease and should not be ignored.
How can you tell if you have periodontal disease?
Periodontal disease causes gums to pull away from teeth, forming pockets that collect bacteria. Symptoms include bleeding, swelling, and tooth loosening. Regular dental checkups can help detect this condition early.
How can you tell if you have infection in gum?
An infection in your gum may cause swelling, redness, and pain. You might notice pus or discharge coming from the affected area. Seek dental care immediately to prevent further damage.
See Also
Identifying Early Signs of Gum Disease Symptoms
The Impact of Stress on Gum Health and Disease
Understanding the Various Stages of Gum Disease
